Back
BackProblem 19a
If two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is 4?
Problem 19b
If two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is 7?
Problem 19c
If two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is
greater than 5?
Problem 19d
If two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is
an odd number?
Problem 20
Experimental Insight 2.1 describes data, collected by a genetics class like yours, on the numbers of kernels of different colors in bicolor corn. To test the hypothesis that the presence of kernels of different colors in each ear is the result of the segregation of two alleles of a single gene, the class counted 12,356 kernels and found that 9304 were yellow and 3052 were white. Use chi-square analysis to evaluate the fit between the segregation hypothesis and the class results.
Problem 21a
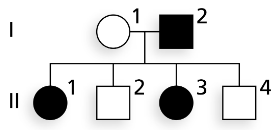
The accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of a phenotypic character. Using B to represent a dominant allele and b to represent a recessive allele,
Give the genotype(s) possible for each member of the family, assuming the trait is autosomal dominant.
Problem 21b
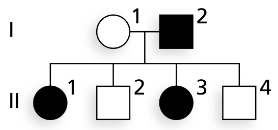
The accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of a phenotypic character. Using B to represent a dominant allele and b to represent a recessive allele,
Give the genotype(s) possible for each member of the family, assuming the trait is autosomal recessive.
Problem 22a
The seeds in bush bean pods are each the product of an independent fertilization event. Green seed color is dominant to white seed color in bush beans. If a heterozygous plant with green seeds self-fertilizes, what is the probability that 6 seeds in a single pod of the progeny plant will consist of 3 green and 3 white seeds?
Problem 22b
The seeds in bush bean pods are each the product of an independent fertilization event. Green seed color is dominant to white seed color in bush beans. If a heterozygous plant with green seeds self-fertilizes, what is the probability that 6 seeds in a single pod of the progeny plant will consist of all green seeds?
Problem 22c
The seeds in bush bean pods are each the product of an independent fertilization event. Green seed color is dominant to white seed color in bush beans. If a heterozygous plant with green seeds self-fertilizes, what is the probability that 6 seeds in a single pod of the progeny plant will consist of at least 1 white seed?
Problem 23a
List all the different gametes that are possible from the following genotypes.
AABbCcDd
Problem 23b
List all the different gametes that are possible from the following genotypes.
AabbCcDD
Problem 23c
List all the different gametes that are possible from the following genotypes.
AaBbCcDd
Problem 23d
List all the different gametes that are possible from the following genotypes.
AabbCCdd
Problem 24a
Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected proportions of the following progeny?
A–B–C–D–
Problem 24b
Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected proportions of the following progeny?
AabbCcDd
Problem 24c
Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected proportions of the following progeny?
A phenotype identical to either parent
Problem 24d
Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected proportions of the following progeny?
A–B–ccdd
Problem 25
Blue moon beans produce beans that are either the dominant color blue or the recessive color white. The bean pods for this species always contain four seeds each. If two heterozygous plants that each have the Bb genotype are crossed, what are the predicted frequencies of each of the five outcome classes for combinations of blue and white seeds in pods?
Problem 26
In the fruit fly Drosophila, a rudimentary wing called 'vestigial' and dark body color called 'ebony' are inherited as independently assorting genes and are recessive to their dominant counterparts full wing and gray body color. Dihybrid dominant-phenotype males and females are crossed, and 3200 progeny are produced. How many progeny flies are expected to be found in each phenotypic class?
Problem 27a
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. The three genes have dominant and recessive alleles, with tall (T) dominant to short (t), round (R) dominant to wrinkled (r), and yellow (G) dominant to green (g).
If a true-breeding tall, wrinkled, yellow plant is crossed to a true-breeding short, round, green plant, what phenotypic ratios are expected in the F1 and F2?
Problem 27b
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. The three genes have dominant and recessive alleles, with tall (T) dominant to short (t), round (R) dominant to wrinkled (r), and yellow (G) dominant to green (g).
What proportion of the F2 are expected to be tall, wrinkled, yellow? ttRRGg?
Problem 27c
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. The three genes have dominant and recessive alleles, with tall (T) dominant to short (t), round (R) dominant to wrinkled (r), and yellow (G) dominant to green (g).
What proportion of the that produce round, green seeds (regardless of the height of the plant) are expected to breed true?
Problem 28a
A variety of pea plant called Blue Persian produces a tall plant with blue seeds. A second variety of pea plant called Spanish Dwarf produces a short plant with white seed. The two varieties are crossed, and the resulting seeds are collected. All of the seeds are white; and when planted, they produce all tall plants. These tall F₁ plants are allowed to self-fertilize. The results for seed color and plant stature in the F₂ generation are as follows:
Which phenotypes are dominant, and which are recessive? Why?
Problem 28b
A variety of pea plant called Blue Persian produces a tall plant with blue seeds. A second variety of pea plant called Spanish Dwarf produces a short plant with white seed. The two varieties are crossed, and the resulting seeds are collected. All of the seeds are white; and when planted, they produce all tall plants. These tall F₁ plants are allowed to self-fertilize. The results for seed color and plant stature in the F₂ generation are as follows:
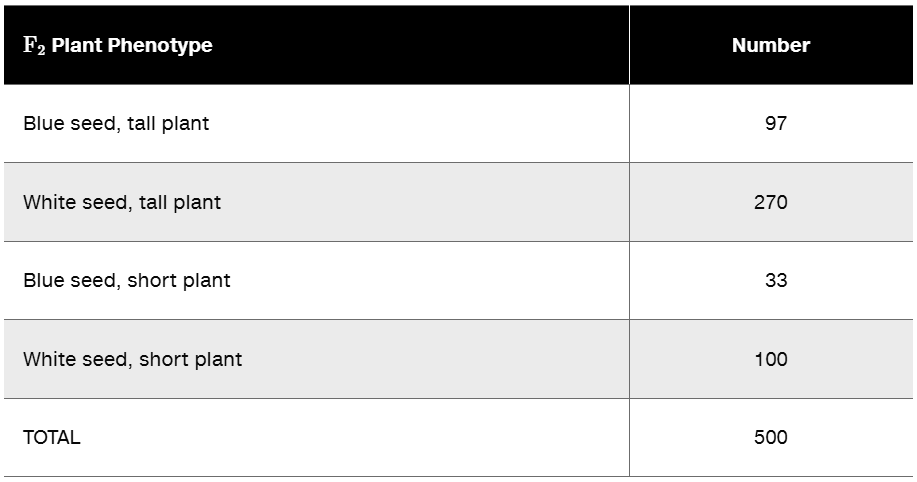
F₂ Plant Phenotype Number
Blue seed, tall plant. 97
White seed, tall plant 270
Blue seed, short plant 33
White seed, short plant 100
TOTAL 500
What is the expected distribution of phenotypes in the F₂ generation?
Problem 28c
A variety of pea plant called Blue Persian produces a tall plant with blue seeds. A second variety of pea plant called Spanish Dwarf produces a short plant with white seed. The two varieties are crossed, and the resulting seeds are collected. All of the seeds are white; and when planted, they produce all tall plants. These tall F₁ plants are allowed to self-fertilize. The results for seed color and plant stature in the F₂ generation are as follows:
F₂ Plant Phenotype Number
Blue seed, tall plant. 97
White seed, tall plant 270
Blue seed, short plant 33
White seed, short plant 100
TOTAL 500
State the hypothesis being tested in this experiment.
Problem 28d
A variety of pea plant called Blue Persian produces a tall plant with blue seeds. A second variety of pea plant called Spanish Dwarf produces a short plant with white seed. The two varieties are crossed, and the resulting seeds are collected. All of the seeds are white; and when planted, they produce all tall plants. These tall F₁ plants are allowed to self-fertilize. The results for seed color and plant stature in the F₂ generation are as follows:
F₂ Plant Phenotype Number
Blue seed, tall plant. 97
White seed, tall plant 270
Blue seed, short plant 33
White seed, short plant 100
TOTAL 500
Examine the data in the table by the chi-square test and determine whether they conform to expectations of the hypothesis.
Problem 29
In tomato plants, the production of red fruit color is under the control of an allele R. Yellow tomatoes are rr. The dominant phenotype for fruit shape is under the control of an allele T, which produces two lobes. Multilobed fruit, the recessive phenotype, has the genotype tt. Two different crosses are made between parental plants of unknown genotype and phenotype. Use the progeny phenotype ratios to determine the genotypes and phenotypes of each parent.
Cross 1 progeny:
3/8 two-lobed, Red
3/8 two-lobed, yellow
1/8 multilobed, Red
1/8 multilobed, Yellow
Cross 2 progeny:
1/4 two-lobed, Red
1/4 two-lobed, yellow
1/4 multilobed, Red
1/4 multilobed, yellow
Problem 29
During your work as a laboratory assistant in the research facilities of Dr. O. Sophila, a world-famous geneticist, you come across an unusual bottle of fruit flies. All the flies in the bottle appear normal when they are in an incubator set at 22°C. When they are moved to a 30°C incubator, however, a few of the flies slowly become paralyzed; and after about 20 to 30 minutes, they are unable to move. Returning the flies to 22°C restores their ability to move after about 30 to 45 minutes.
With Dr. Sophila's encouragement, you set up 10 individual crosses between single male and female flies that exhibit the unusual behavior. Among 812 progeny, 598 exhibit the unusual behavior and 214 do not. When you leave one of the test bottles in the 30°C incubator too long, you discover that more than 2 hours at high temperature kills the paralyzed flies. When you tell this to Dr. Sophila, he says, 'Aha! I know how to explain this condition.' What is his explanation?
Problem 30a
A male and a female are each heterozygous for both cystic fibrosis (CF) and phenylketonuria (PKU). Both conditions are autosomal recessive, and they assort independently.
What proportion of the children of this couple will have neither condition?