Back
Back Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage
Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and BacteriophageProblem 17a
Identify which of the following lac operon haploid genotypes transcribe operon genes inducibly and which transcribe genes constitutively. Indicate whether the strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
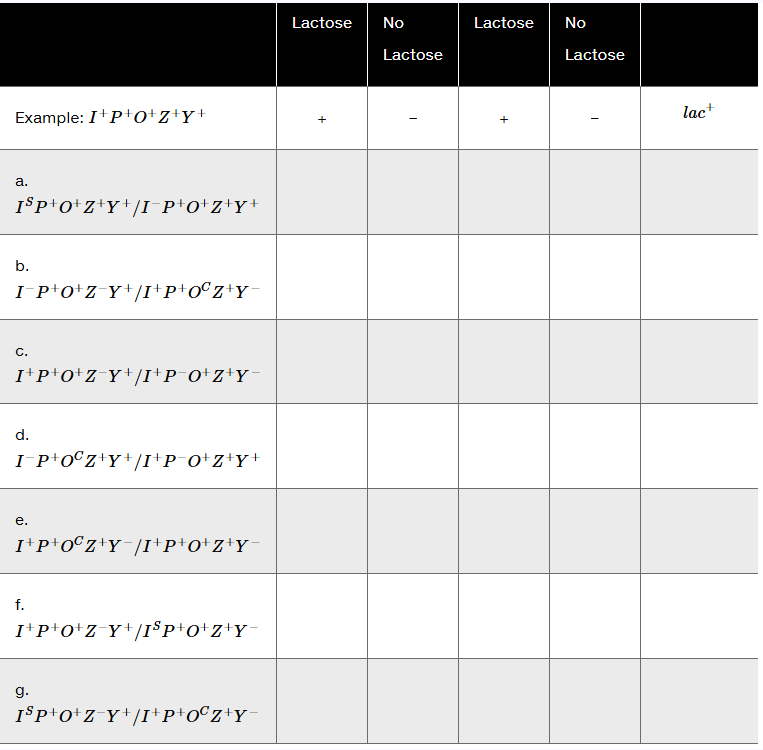
I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁻
Problem 17b
Identify which of the following lac operon haploid genotypes transcribe operon genes inducibly and which transcribe genes constitutively. Indicate whether the strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
I⁺ P⁺ Oᶜ Z⁻ Y⁺
Problem 17c
Identify which of the following lac operon haploid genotypes transcribe operon genes inducibly and which transcribe genes constitutively. Indicate whether the strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
I⁻ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁺
Problem 17d
Identify which of the following lac operon haploid genotypes transcribe operon genes inducibly and which transcribe genes constitutively. Indicate whether the strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
I⁺ P⁻ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁺
Problem 17e
Identify which of the following lac operon haploid genotypes transcribe operon genes inducibly and which transcribe genes constitutively. Indicate whether the strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁻ Y⁺
Problem 17f
Identify which of the following lac operon haploid genotypes transcribe operon genes inducibly and which transcribe genes constitutively. Indicate whether the strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
I⁺ P⁺ Oᶜ Z⁺ Y⁻
Problem 17g
Identify which of the following lac operon haploid genotypes transcribe operon genes inducibly and which transcribe genes constitutively. Indicate whether the strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
I⁺ P⁺ Oᶜ Z⁺ Y⁺
Problem 18
Complete the accompanying table, indicating whether functionally active -galactosidase and permease are produced in the presence and absence of lactose. Use '+' to indicate the presence of a functional enzyme and '−' to indicate its absence. Indicate whether the partial diploid strain is lac⁺ (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac⁻ (cannot grow on lactose medium).
Problem 19a
List possible genotypes for lac operon haploids that have the following phenotypic characteristics:
The operon genes are constitutively transcribed, but the strain is unable to grow on a lactose medium. List two possible genotypes for this phenotype.
Problem 19b
List possible genotypes for lac operon haploids that have the following phenotypic characteristics:
The operon genes are never transcribed above a basal level, and the strain is unable to grow on a lactose medium. List two possible genotypes for this phenotype.
Problem 19c
List possible genotypes for lac operon haploids that have the following phenotypic characteristics:
The operon genes are inducibly transcribed, but the strain is unable to grow on a lactose medium. List one possible genotype for this phenotype.
Problem 19d
List possible genotypes for lac operon haploids that have the following phenotypic characteristics:
The operon genes are constitutively transcribed, and the strain grows on lactose medium. List two possible genotypes for this phenotype.
Problem 20a
Suppose each of the genotypes you listed in parts (a) and (b) of Problem 19 are placed in a partial diploid genotype along with a chromosome that has a fully wild-type lac operon.
Will the transcription of operon genes in each partial diploid be inducible or constitutive?
Problem 20b
Suppose each of the genotypes you listed in parts (a) and (b) of Problem 19 are placed in a partial diploid genotype along with a chromosome that has a fully wild-type lac operon.
Which partial diploids will be able to grow on a lactose medium?
Problem 21
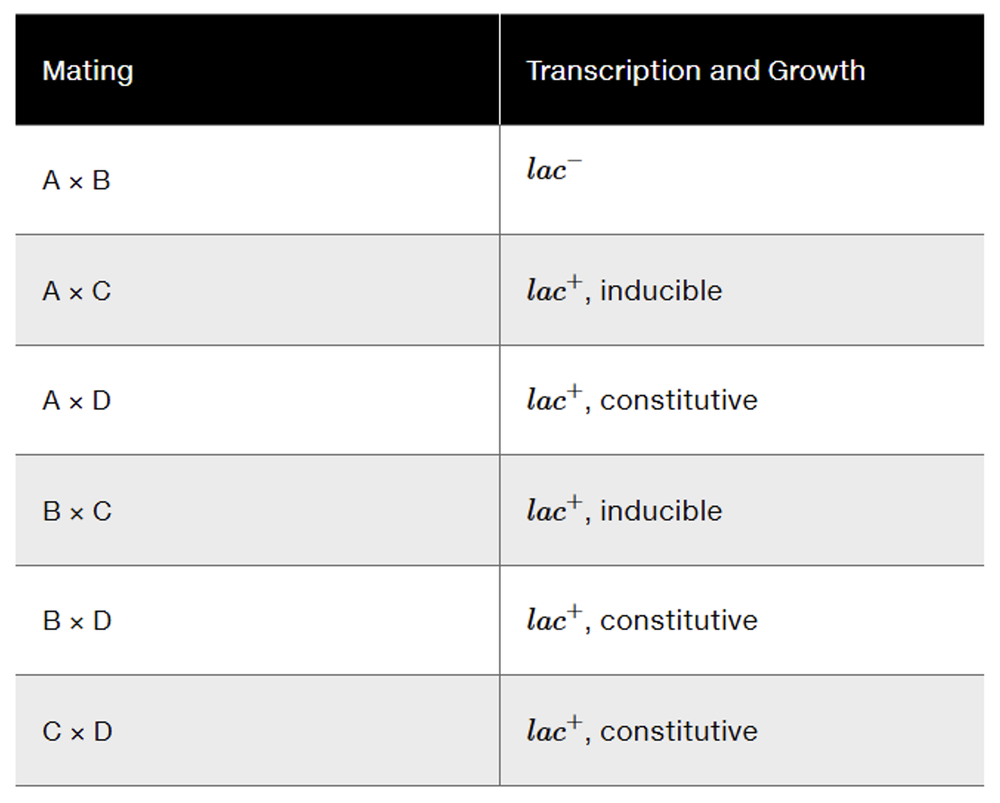
Four independent lac⁻ mutants (mutants A to D) are isolated in haploid strains of E. coli. The strains have the following phenotypic characteristics:
Mutant A is lac⁻, but transcription1 of operon genes is induced by lactose.
Mutant B is lac⁻ and has uninducible2 transcription of operon genes.
Mutant C is lac⁺ and has constitutive3 transcription of operon genes.
Mutant D is lac⁺ and has constitutive3 transcription of operon genes.
A microbiologist develops donor and recipient varieties of each mutant strain and crosses them with the results shown below. The table indicates whether inducible, constitutive, or noninducible transcription occurs, along with lac+ and lac⁻ growth habit for each partial diploid. Assume each strain has a single mutation.
Use this information to identify which lac operon gene is mutated in each strain.
Problem 22a
Suppose the lac operon partial diploid cap⁻ I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁻ Y⁺/ cap⁺ I⁻ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁻ is grown.
Will this partial diploid strain grow on a lactose medium?
Problem 22b
Suppose the lac operon partial diploid cap⁻ I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁻ Y⁺/ cap⁺ I⁻ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁻ is grown.
Is transcription of β-galactosidase and permease inducible, constitutive, or noninducible?
Problem 22c
Suppose the lac operon partial diploid cap⁻ I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁻ Y⁺/ cap⁺ I⁻ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁻ is grown.
Explain how genetic complementation contributes to the growth habit of this strain.
Problem 23
What is a riboswitch? Describe the riboswitch mechanism that regulates transcription of the thi operon in B. subtilus. What parallels can you see between this mechanism and the regulation of transcription of the trp operon in E. coli?
Problem 24
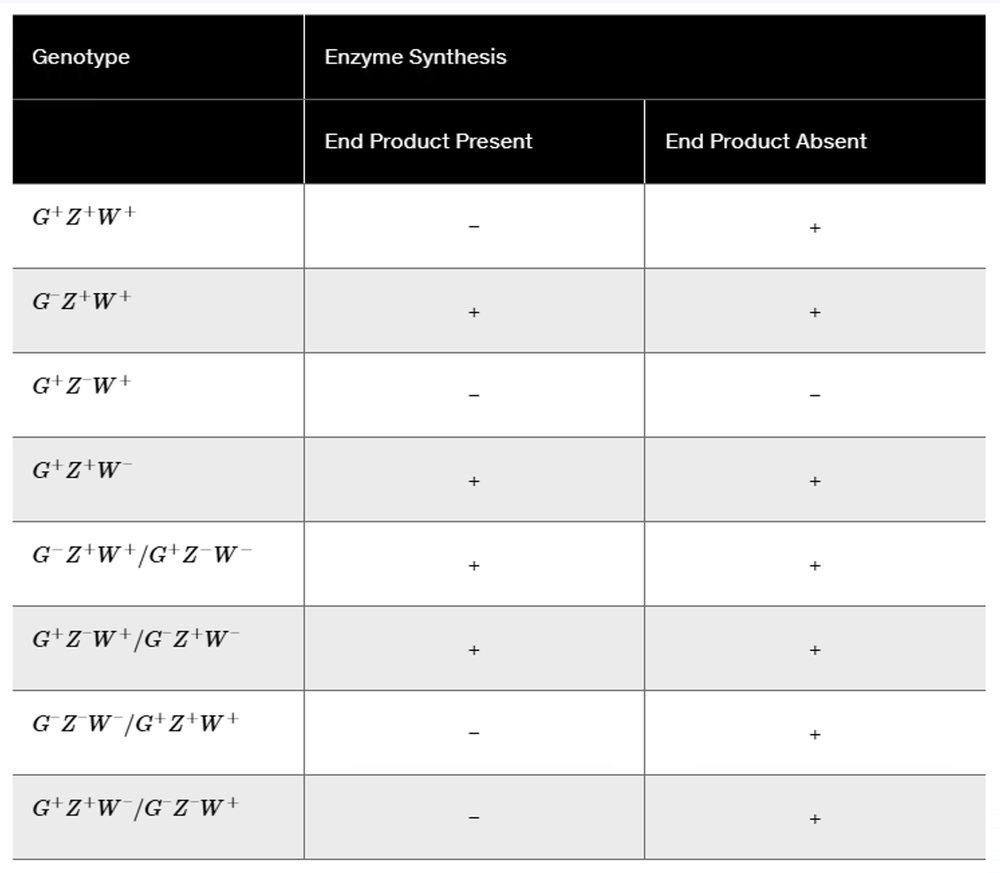
A repressible operon system, like the trp operon, contains three genes, G, Z, and W. Operon genes are synthesized when the end product of the operon synthesis pathway is absent, but there is no synthesis when the end product is present. One of these genes is an operator, one is a regulatory protein, and the other is a structural enzyme involved in synthesis of the end product. In the table below, '+' indicates that the enzyme is synthesized by the operon and '−' means that no enzyme synthesis occurs. Use this information to determine which gene corresponds to each operon function.
Problem 25a
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
Region 3 is deleted.
Problem 25b
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
Region 4 is deleted.
Problem 25c
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
The entire trpL region is deleted.
Problem 25d
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
The start (AUG) codon of the trpL polypeptide is deleted.
Problem 25e
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
Two nucleotides are inserted into the trpL region immediately after the polypeptide stop codon.
Problem 25f
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
Twenty nucleotides are inserted into the trpL region immediately after the polypeptide stop codon.
Problem 25g
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
Ten nucleotides are inserted between regions 2 and 3 of trpL.
Problem 25h
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
Two nucleotides are inserted immediately following the polypeptide start codon.
Problem 25i
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
The entire polypeptide coding sequence of trpL is deleted.
Problem 25j
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning.
The eight uracil nucleotides immediately following region 4 are deleted.