Back
Back Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 10 - Eukaryotic Chromosome Abnormalities and Molecular Organization
Ch. 10 - Eukaryotic Chromosome Abnormalities and Molecular OrganizationProblem 10a
A researcher interested in studying a human gene on chromosome 21 and another gene on the X chromosome uses FISH probes to locate each gene. The chromosome 21 probe produces green fluorescent color, and the X chromosome probe produces red fluorescent color.
If the subject studied is female, how many green and red spots will be detected? Explain your answer.
Problem 10b
A researcher interested in studying a human gene on chromosome 21 and another gene on the X chromosome uses FISH probes to locate each gene. The chromosome 21 probe produces green fluorescent color, and the X chromosome probe produces red fluorescent color.
If the subject studied is male, how many green and red spots will be detected? Explain your answer.
Problem 11
In what way does position effect variegation (PEV) of Drosophila eye color indicate that chromatin state can affect gene transcription?
Problem 12a
A pair of homologous chromosomes in Drosophila has the following content (single letters represent genes):
Chromosome 1 RNMDHBGKWU
Chromosome 2 RNMDHBDHBGKWU
What term best describes this situation?
Problem 12b
A pair of homologous chromosomes in Drosophila has the following content (single letters represent genes):
Chromosome 1 RNMDHBGKWU
Chromosome 2 RNMDHBDHBGKWU
Diagram the pairing of these homologous chromosomes in prophase I.
Problem 12c
A pair of homologous chromosomes in Drosophila has the following content (single letters represent genes):
Chromosome 1 RNMDHBGKWU
Chromosome 2 RNMDHBDHBGKWU
What term best describes the unusual structure that forms during pairing of these chromosomes?
Problem 12d
A pair of homologous chromosomes in Drosophila has the following content (single letters represent genes):
Chromosome 1 RNMDHBGKWU
Chromosome 2 RNMDHBDHBGKWU
How does the pairing diagrammed in part (b) differ from the pairing of chromosomes in an inversion heterozygote?
Problem 13a
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Diagram the pairing of these chromosomes in prophase I.
Problem 13b
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by alternate segregation. Which, if any, of these gametes are viable?
Problem 13c
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by adjacent-1 segregation. Which, if any, of these gametes are viable?
Problem 13d
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by adjacent-2 segregation. Which if any of these gametes are viable?
Problem 13e
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Among the three segregation patterns, which is least likely to occur? Why?
Problem 14a
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis has an idea he thinks will be a boon to agriculture. He wants to create the 'pomato,' a hybrid between a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) that has 12 chromosomes and a potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 48 chromosomes. Dr. Dopsis is hoping his new pomato will have tuber growth like a potato and the fruit production of a tomato. He joins a haploid gamete from each species to form a hybrid and then induces doubling of chromosome number. How many chromosomes will the hybrid have before chromosome doubling?
Problem 14b
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis has an idea he thinks will be a boon to agriculture. He wants to create the 'pomato,' a hybrid between a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) that has 12 chromosomes and a potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 48 chromosomes. Dr. Dopsis is hoping his new pomato will have tuber growth like a potato and the fruit production of a tomato. He joins a haploid gamete from each species to form a hybrid and then induces doubling of chromosome number. Will this hybrid be infertile?
Problem 14c
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis has an idea he thinks will be a boon to agriculture. He wants to create the 'pomato,' a hybrid between a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) that has 12 chromosomes and a potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 48 chromosomes. Dr. Dopsis is hoping his new pomato will have tuber growth like a potato and the fruit production of a tomato. He joins a haploid gamete from each species to form a hybrid and then induces doubling of chromosome number.
How many chromosomes will the polyploid have after chromosome doubling?
Problem 14d
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis has an idea he thinks will be a boon to agriculture. He wants to create the 'pomato,' a hybrid between a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) that has 12 chromosomes and a potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 48 chromosomes. Dr. Dopsis is hoping his new pomato will have tuber growth like a potato and the fruit production of a tomato. He joins a haploid gamete from each species to form a hybrid and then induces doubling of chromosome number.
Can Dr. Dopsis be sure the polyploid will have the characteristics he wants? Why or why not?
Problem 15a
A normal chromosome and its homolog carrying a paracentric inversion are shown here. The dot (·) represents the centromere.
Normal ABC • DEFGHIJK
Inversion abc • djihgfe
Diagram the alignment of chromosomes during prophase I.
Problem 15b
A normal chromosome and its homolog carrying a paracentric inversion are shown here. The dot (·) represents the centromere.
Normal ABC • DEFGHIJK
Inversion abc • djihgfe
Assume a crossover takes place in the region between F and G. Identify the gametes that are formed following this crossover, and indicate which, if any, gametes are viable.
Problem 15c
A normal chromosome and its homolog carrying a paracentric inversion are shown here. The dot (·) represents the centromere.
Normal ABC • DEFGHIJK
Inversion abc • djihgfe
Assume a crossover takes place in the region between A and B. Identify the gametes that are formed by this crossover event, and indicate which, if any, gametes are viable.
Problem 16a
The accompanying chromosome diagram represents a eukaryotic chromosome prepared with Giemsa stain. Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions of the chromosome, and label the chromosome's centromeric and telomeric regions.
What term best describes the shape of this chromosome?
Problem 16b
The accompanying chromosome diagram represents a eukaryotic chromosome prepared with Giemsa stain. Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions of the chromosome, and label the chromosome's centromeric and telomeric regions.
Do you expect the centromeric region to contain heterochromatin? Why or why not?
Problem 16c
The accompanying chromosome diagram represents a eukaryotic chromosome prepared with Giemsa stain. Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions of the chromosome, and label the chromosome's centromeric and telomeric regions.
Why are expressed genes not found in the telomeric region of chromosomes?
Problem 16d
The accompanying chromosome diagram represents a eukaryotic chromosome prepared with Giemsa stain. Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions of the chromosome, and label the chromosome's centromeric and telomeric regions.
Are you more likely to find the DNA sequence encoding the digestive enzyme amylase in a heterochromatic, euchromatic, centromeric, or telomeric region? Explain your reasoning.
Problem 17
Histone protein H4 isolated from pea plants and cow thymus glands contains 102 amino acids in both cases. A total of 100 of the amino acids are identical between the two species. Give an evolutionary explanation for this strong amino acid sequence identity based on what you know about the functions of histones and nucleosomes.
Problem 18
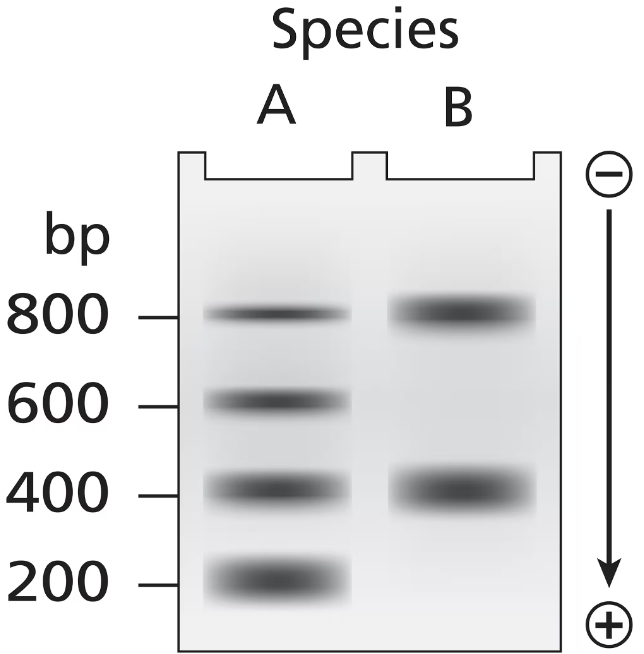
A survey of organisms living deep in the ocean reveals two new species whose DNA is isolated for analysis. DNA samples from both species are treated to remove nonhistone proteins. Each DNA sample is then treated with DNase I that cuts DNA not protected by histone proteins but is unable to cut DNA bound by histone proteins. Following DNase I treatment, DNA samples are subjected to gel electrophoresis, and the gels are stained to visualize all DNA bands in the gel. The staining patterns of DNA bands from each species are shown in the figure. The number of base pairs in small DNA fragments is shown at the left of the gel. Interpret the gel results in terms of chromatin organization and the spacing of nucleosomes in the chromatin of each species.
Problem 19
In humans that are XX/XO mosaics, the phenotype is highly variable, ranging from females who have classic Turner syndrome symptoms to females who are essentially normal. Likewise, XY/XO mosaics have phenotypes that range from Turner syndrome females to essentially normal males. How can the wide range of phenotypes be explained for these sex-chromosome mosaics?
Problem 20
A plant breeder would like to develop a seedless variety of cucumber from two existing lines. Line A is a tetraploid line, and line B is a diploid line. Describe the breeding strategy that will produce a seedless line, and support your strategy by describing the results of crosses.
Problem 21
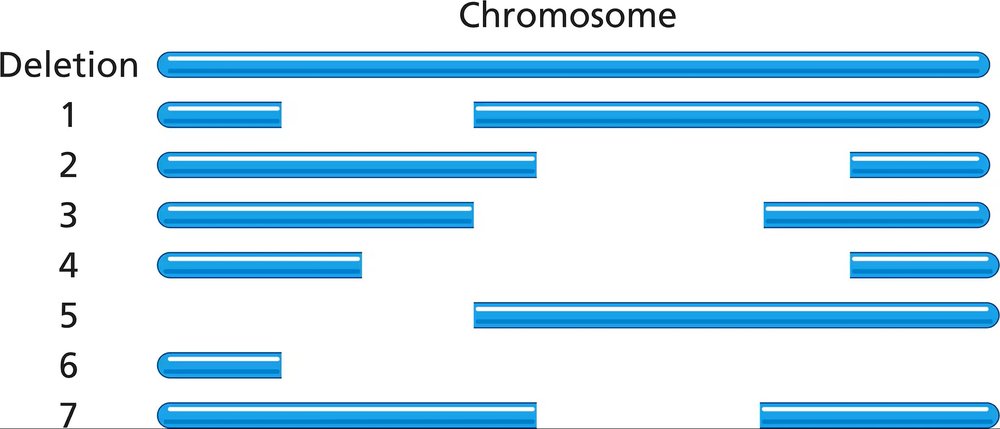
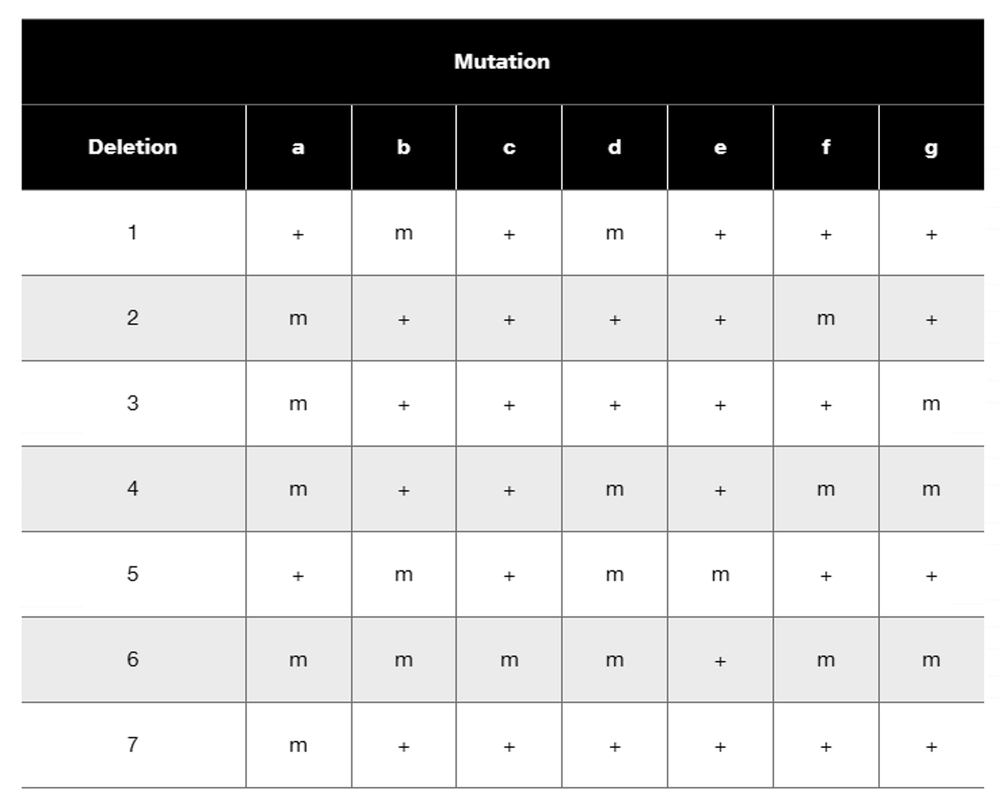
In Drosophila, seven partial deletions (1 to 7) shown as gaps in the following diagram have been mapped on a chromosome. This region of the chromosome contains genes that express seven recessive mutant phenotypes, identified in the following table as a through g. A researcher wants to determine the location and order of genes on the chromosome, so he sets up a series of crosses in which flies homozygous for a mutant allele are crossed with flies homozygous for a partial deletion. The progeny are scored to determine whether they have the mutant phenotype ('m' in the table) or the wild-type phenotype ('+' in the table). Use the partial deletion map and the table of progeny phenotypes to determine the order of genes on the chromosome.
Problem 22a
Two experimental varieties of strawberry are produced by crossing a hexaploid line that contains 48 chromosomes and a tetraploid line that contains 32 chromosomes. Experimental variety 1 contains 40 chromosomes, and experimental variety 2 contains 56 chromosomes.
Do you expect both experimental lines to be fertile? Why or why not?
Problem 22b
Two experimental varieties of strawberry are produced by crossing a hexaploid line that contains 48 chromosomes and a tetraploid line that contains 32 chromosomes. Experimental variety 1 contains 40 chromosomes, and experimental variety 2 contains 56 chromosomes.
How many chromosomes from the hexaploid line are contributed to experimental variety 1? To experimental variety 2?