Back
BackProblem 24b
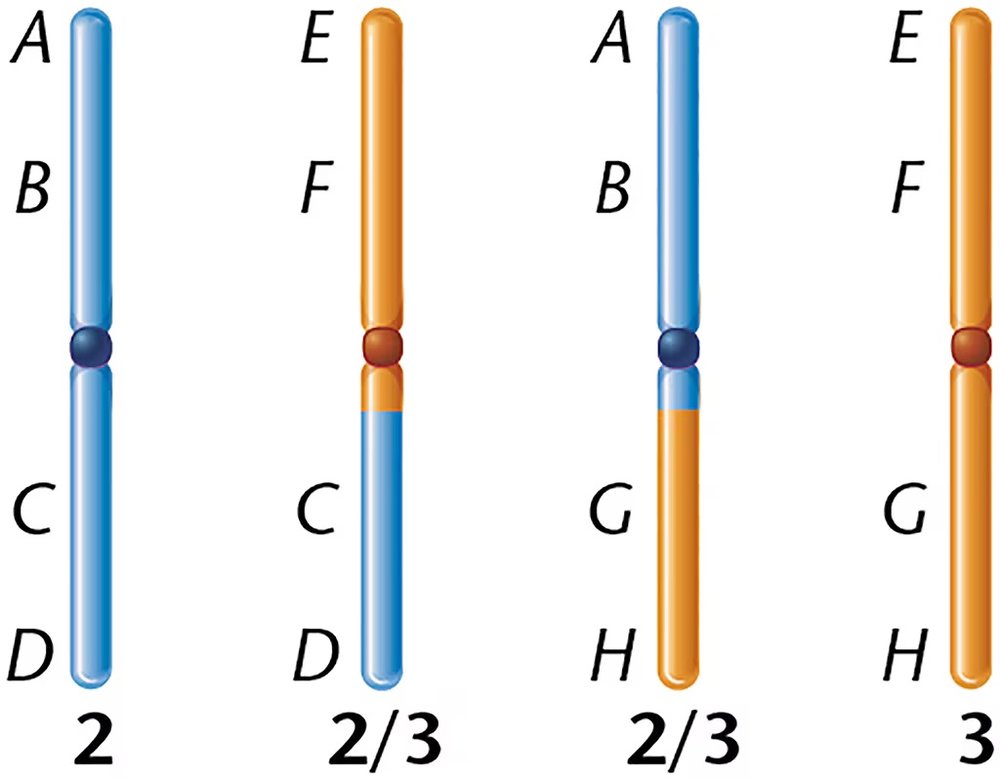
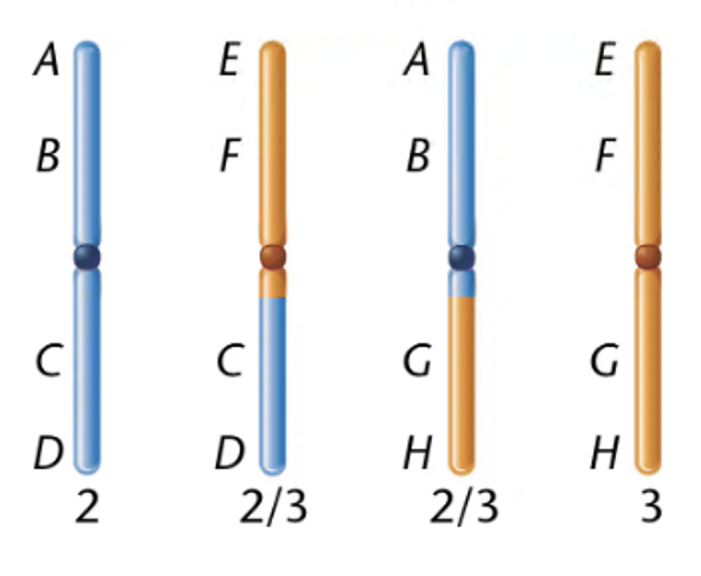
A woman who sought genetic counseling is found to be heterozygous for a chromosomal rearrangement between the second and third chromosomes. Her chromosomes, compared to those in a normal karyotype, are diagrammed to the right.
Using a drawing, demonstrate how these chromosomes would pair during meiosis. Be sure to label the different segments of the chromosomes.
Problem 24c
A woman who sought genetic counseling is found to be heterozygous for a chromosomal rearrangement between the second and third chromosomes. Her chromosomes, compared to those in a normal karyotype, are diagrammed to the right.
This woman is phenotypically normal. Does this surprise you? Why or why not? Under what circumstances might you expect a phenotypic effect of such a rearrangement?
Problem 25
The woman in Problem 24 has had two miscarriages. She has come to you, an established genetic counselor, with these questions:
Is there a genetic explanation of her frequent miscarriages?
Should she abandon her attempts to have a child of her own?
If not, what is the chance that she could have a normal child? Provide an informed response to her concerns.
Problem 26
In a recent cytogenetic study on 1021 cases of Down syndrome, 46 were the result of translocations, the most frequent of which was symbolized as t(14;21). What does this symbol represent, and how many chromosomes would you expect to be present in t(14;21) Down syndrome individuals?
Problem 27a
A boy with Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) is born to a mother who is phenotypically normal and a father who has the X-linked skin condition called anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. The mother's skin is completely normal with no signs of the skin abnormality. In contrast, her son has patches of normal skin and patches of abnormal skin.
Which parent contributed the abnormal gamete?
Problem 27b
A boy with Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) is born to a mother who is phenotypically normal and a father who has the X-linked skin condition called anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. The mother's skin is completely normal with no signs of the skin abnormality. In contrast, her son has patches of normal skin and patches of abnormal skin.
Using the appropriate genetic terminology, describe the meiotic mistake that occurred. Be sure to indicate in which division the mistake occurred.
Problem 27c
A boy with Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) is born to a mother who is phenotypically normal and a father who has the X-linked skin condition called anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. The mother's skin is completely normal with no signs of the skin abnormality. In contrast, her son has patches of normal skin and patches of abnormal skin.
Using the appropriate genetic terminology, explain the son's skin phenotype.
- Most cases of Turner syndrome are attributed to nondisjunction of one or more of the sex chromosomes during gametogenesis, from either the male or female parent. However, some females possess a rare form of Turner syndrome in which some of the cells of the body (somatic cells) lack an X chromosome, while other cells have the normal two X chromosomes. Often detected in blood and/or skin cells, such individuals with mosaic Turner syndrome may exhibit relatively mild symptoms. An individual may be specified as 45,X(20)/46,XX(80) if, for example, 20 percent of the cells examined were X monosomic. How might mitotic events cause such mosaicism, and what parameter(s) would likely determine the percentages and distributions of X0 cells?
Problem 28
Problem 29
A 3-year-old child exhibited some early indication of Turner syndrome, which results from a 45,X chromosome composition. Karyotypic analysis demonstrated two cell types: 46,XX (normal) and 45,X. Propose a mechanism for the origin of this mosaicism.
Problem 30
A normal female is discovered with 45 chromosomes, one of which exhibits a Robertsonian translocation containing most of chromosomes 15 and 21. Discuss the possible outcomes in her offspring when her husband contains a normal karyotype.