Cat breeders are aware that kittens expressing the X-linked calico coat pattern and tortoiseshell pattern are almost invariably females. Why are they certain of this?
Ch. 7 - Sex Determination and Sex Chromosomes

Chapter 7, Problem 18
Can the Lyon hypothesis be tested in a human female who is homozygous for one allele of the X-linked G6PD gene? Why, or why not?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the Lyon hypothesis, which states that in female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated in each cell early in development, leading to dosage compensation between males (XY) and females (XX).
Step 2: Recognize that the Lyon hypothesis can be tested by observing phenotypic mosaicism in heterozygous females for an X-linked gene, where different cells express different alleles depending on which X chromosome is inactivated.
Step 3: Consider the genetic status of the female in question: she is homozygous for one allele of the X-linked G6PD gene, meaning both X chromosomes carry the same allele.
Step 4: Analyze the consequence of homozygosity: since both X chromosomes have the same allele, X-inactivation will not produce any phenotypic mosaicism because all cells express the same allele regardless of which X is inactivated.
Step 5: Conclude that the Lyon hypothesis cannot be effectively tested in this homozygous female using the G6PD gene, because the lack of allelic variation prevents observation of differential expression due to X-inactivation.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lyon Hypothesis (X-Chromosome Inactivation)
The Lyon hypothesis proposes that in female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated in each cell early in development, leading to dosage compensation between males and females. This inactivation is stable and results in mosaic expression of X-linked genes in heterozygous females.
Recommended video:
Guided course

X-Inactivation
X-Linked Genes and Allelic Variation
X-linked genes, like G6PD, are located on the X chromosome. Females have two alleles for these genes, which can be different (heterozygous) or the same (homozygous). The presence of different alleles allows observation of differential expression due to X inactivation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
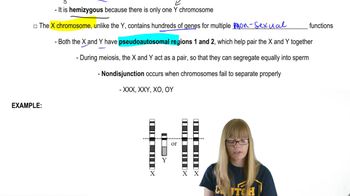
Sex-Linked Genes
Testing the Lyon Hypothesis in Homozygous Females
In a female homozygous for one allele of an X-linked gene, both X chromosomes carry the same allele, so X inactivation cannot be detected by phenotypic differences. Therefore, the Lyon hypothesis cannot be directly tested in such individuals because there is no observable mosaicism.
Recommended video:
Guided course
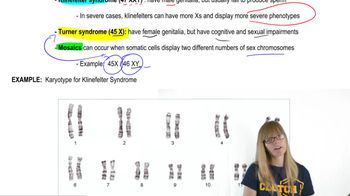
Human Sex Chromosomes
Related Practice
Textbook Question
3
views
Textbook Question
What is a Barr body, and where is it found in a cell?
3
views
Textbook Question
Indicate the expected number of Barr bodies in interphase cells of individuals with Klinefelter syndrome, Turner syndrome, and karyotypes 47, XYY, 47, XXX, and 48, XXXX.
Textbook Question
Define the Lyon hypothesis.
2
views
Textbook Question
Predict the potential effect of the Lyon hypothesis on the retina of a human female heterozygous for the X-linked red-green color blindness trait.
3
views
Textbook Question
In mice, the Sry gene is located on the Y chromosome very close to one of the pseudoautosomal regions that pairs with the X chromosome during male meiosis. Given this information, propose a model to explain the generation of unusual males who have two X chromosomes (with an Sry-containing piece of the Y chromosome attached to one X chromosome).
3
views
