Back
BackProblem 38
In Dexter and Kerry cattle, animals may be polled (hornless) or horned. The Dexter animals have short legs, whereas the Kerry animals have long legs. When many offspring were obtained from matings between polled Kerrys and horned Dexters, half were found to be polled Dexters and half polled Kerrys. When these two types of F₁ cattle were mated to one another, the following F₂ data were obtained:
3/8 polled Dexters
3/8 polled Kerrys
1/8 horned Dexters
1/8 horned Kerrys
A geneticist was puzzled by these data and interviewed farmers who had bred these cattle for decades. She learned that Kerrys were true breeding. Dexters, on the other hand, were not true breeding and never produced as many offspring as Kerrys. Provide a genetic explanation for these observations.
Problem 39a
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding lines of frogs. One line croaks by uttering 'rib-it rib-it' and has purple eyes. The other line croaks more softly by muttering 'knee-deep knee-deep' and has green eyes. With a newfound freedom of inquiry, the geneticist mated the two types of frogs, producing F₁ frogs that were all utterers and had blue eyes. A large F₂ generation then yielded the following ratios:
27/64 blue-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
12/64 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
9/64 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
9/64 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
4/64 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/64 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
How many total gene pairs are involved in the inheritance of both traits? Support your answer.
Problem 39b
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding lines of frogs. One line croaks by uttering 'rib-it rib-it' and has purple eyes. The other line croaks more softly by muttering 'knee-deep knee-deep' and has green eyes. With a newfound freedom of inquiry, the geneticist mated the two types of frogs, producing F₁ frogs that were all utterers and had blue eyes. A large F₂ generation then yielded the following ratios:
27/64 blue-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
12/64 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
9/64 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
9/64 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
4/64 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/64 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
Of these, how many are controlling eye color? How can you tell? How many are controlling croaking?
Problem 39c
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding lines of frogs. One line croaks by uttering 'rib-it rib-it' and has purple eyes. The other line croaks more softly by muttering 'knee-deep knee-deep' and has green eyes. With a newfound freedom of inquiry, the geneticist mated the two types of frogs, producing F₁ frogs that were all utterers and had blue eyes. A large F₂ generation then yielded the following ratios:
27/64 blue-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
12/64 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
9/64 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
9/64 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
4/64 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/64 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
Assign gene symbols for all phenotypes and indicate the genotypes of the P₁ and F₁ frogs.
Problem 39d
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding lines of frogs. One line croaks by uttering 'rib-it rib-it' and has purple eyes. The other line croaks more softly by muttering 'knee-deep knee-deep' and has green eyes. With a newfound freedom of inquiry, the geneticist mated the two types of frogs, producing F₁ frogs that were all utterers and had blue eyes. A large F₂ generation then yielded the following ratios:
27/64 blue-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
12/64 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
9/64 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
9/64 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
4/64 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/64 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
Indicate the genotypes of the six F₂ phenotypes.
Problem 39e
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding lines of frogs. One line croaks by uttering 'rib-it rib-it' and has purple eyes. The other line croaks more softly by muttering 'knee-deep knee-deep' and has green eyes. With a newfound freedom of inquiry, the geneticist mated the two types of frogs, producing F₁ frogs that were all utterers and had blue eyes. A large F₂ generation then yielded the following ratios:
27/64 blue-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
12/64 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
9/64 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
9/64 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
4/64 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/64 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
After years of experiments, the geneticist isolated pure-breeding strains of all six F₂ phenotypes. Indicate the F₁ and F₂ phenotypic ratios of the following cross using these pure-breeding strains: blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer x purpled-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer.
Problem 39f
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding lines of frogs. One line croaks by uttering 'rib-it rib-it' and has purple eyes. The other line croaks more softly by muttering 'knee-deep knee-deep' and has green eyes. With a newfound freedom of inquiry, the geneticist mated the two types of frogs, producing F₁ frogs that were all utterers and had blue eyes. A large F₂ generation then yielded the following ratios:
27/64 blue-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
12/64 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
9/64 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
9/64 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
4/64 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/64 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
One set of crosses with his true-breeding lines initially caused the geneticist some confusion. When he crossed true-breeding purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterers with true-breeding green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterers, he often got different results. In some matings, all offspring were blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterers, but in other matings all offspring were purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterers. In still a third mating, 1/2 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterers and 1/2 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterers were observed. Explain why the results differed.
Problem 39g
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding lines of frogs. One line croaks by uttering 'rib-it rib-it' and has purple eyes. The other line croaks more softly by muttering 'knee-deep knee-deep' and has green eyes. With a newfound freedom of inquiry, the geneticist mated the two types of frogs, producing F₁ frogs that were all utterers and had blue eyes. A large F₂ generation then yielded the following ratios:
27/64 blue-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
12/64 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
9/64 blue-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
9/64 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
4/64 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/64 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
In another experiment, the geneticist crossed two purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterers together with the results shown here:
9/16 purple-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
3/16 purple-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
3/16 green-eyed, 'rib-it' utterer
1/16 green-eyed, 'knee-deep' mutterer
What were the genotypes of the two parents?
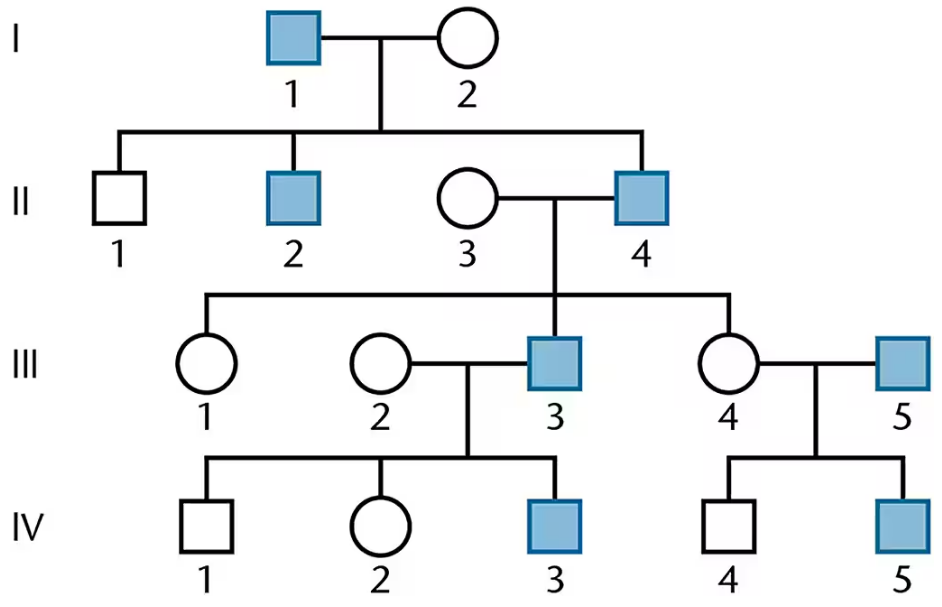
Problem 40
The following pedigree is characteristic of an inherited condition known as male precocious puberty, where affected males show signs of puberty by age 4. Propose a genetic explanation of this phenotype.
Problem 41a
Students taking a genetics exam were expected to answer the following question by converting data to a 'meaningful ratio' and then solving the problem. The instructor assumed that the final ratio would reflect two gene pairs, and most correct answers did. Here is the exam question:
'Flowers may be white, orange, or brown. When plants with white flowers are crossed with plants with brown flowers, all the F₁ flowers are white. For F₂ flowers, the following data were obtained:
48 white
12 orange
4 brown
Convert the F₂ data to a meaningful ratio that allows you to explain the inheritance of color. Determine the number of genes involved and the genotypes that yield each phenotype.'
Solve the problem for two gene pairs. What is the final F₂ ratio?
Problem 41b
Students taking a genetics exam were expected to answer the following question by converting data to a 'meaningful ratio' and then solving the problem. The instructor assumed that the final ratio would reflect two gene pairs, and most correct answers did. Here is the exam question: 'Flowers may be white, orange, or brown. When plants with white flowers are crossed with plants with brown flowers, all the F₁ flowers are white. For F₂ flowers, the following data were obtained:
48 white
12 orange
4 brown
Convert the F₂ data to a meaningful ratio that allows you to explain the inheritance of color. Determine the number of genes involved and the genotypes that yield each phenotype.'
A number of students failed to reduce the ratio for two gene pairs as described above and solved the problem using three gene pairs. When examined carefully, their solution was deemed a valid response by the instructor. Solve the problem using three gene pairs
Problem 41c
Students taking a genetics exam were expected to answer the following question by converting data to a 'meaningful ratio' and then solving the problem. The instructor assumed that the final ratio would reflect two gene pairs, and most correct answers did. Here is the exam question: 'Flowers may be white, orange, or brown. When plants with white flowers are crossed with plants with brown flowers, all the F₁ flowers are white. For F₂ flowers, the following data were obtained:
48 white
12 orange
4 brown
Convert the F₂ data to a meaningful ratio that allows you to explain the inheritance of color. Determine the number of genes involved and the genotypes that yield each phenotype.'
We now have a dilemma. The data are consistent with two alternative mechanisms of inheritance. Propose an experiment that executes crosses involving the original parents that would distinguish between the two solutions proposed by the students. Explain how this experiment would resolve the dilemma.
Problem 42
In four o'clock plants, many flower colors are observed. In a cross involving two true-breeding strains, one crimson and the other white, all of the F₁ generation were rose color. In the F₂, four new phenotypes appeared along with the P₁ and F₁ parental colors. The following ratio was obtained:
1/16 crimson
4/16 rose
2/16 orange
2/16 pale yellow
1/16 yellow
4/16 white
2/16 magenta
Propose an explanation for the inheritance of these flower colors.
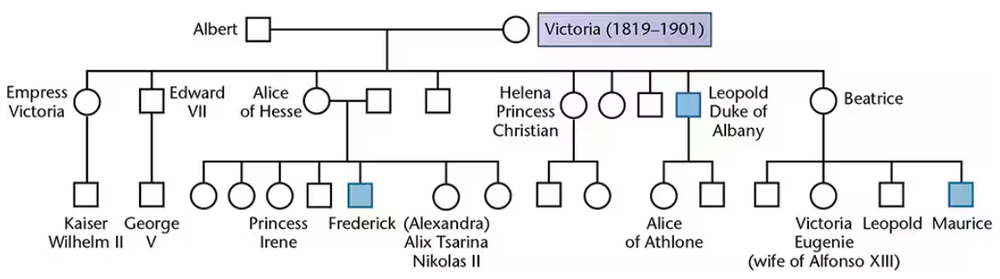
Problem 43
Below is a partial pedigree of hemophilia in the British Royal Family descended from Queen Victoria, who is believed to be the original 'carrier' in this pedigree.
Analyze the pedigree and indicate which females are also certain to be carriers. What is the probability that Princess Irene is a carrier?