Back
BackProblem 29a
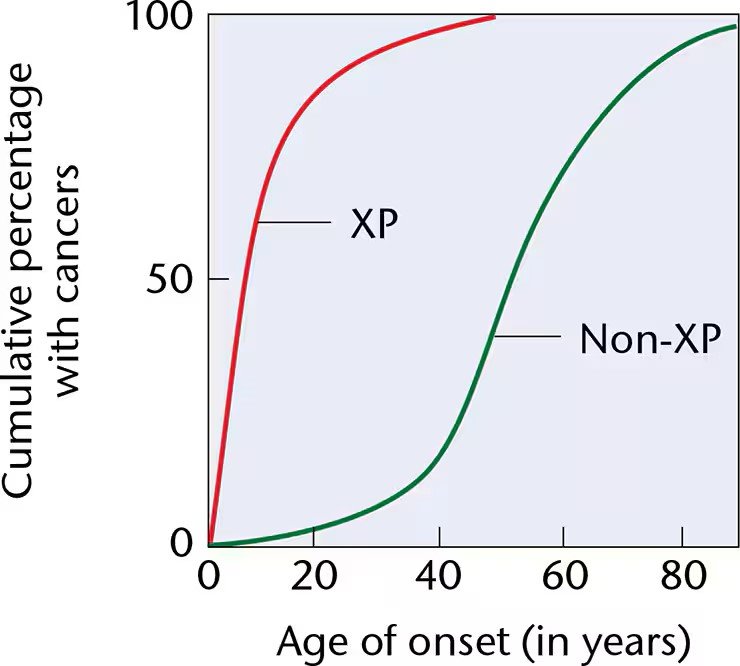
Skin cancer carries a lifetime risk nearly equal to that of all other cancers combined. Following is a graph [modified from K. H. Kraemer (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 94:11 14] depicting the age of onset of skin cancers in patients with or without XP, where the cumulative percentage of skin cancer is plotted against age. The non-XP curve is based on 29,757 cancers surveyed by the National Cancer Institute, and the curve representing those with XP is based on 63 skin cancers from the Xeroderma Pigmentosum Registry.
Provide an overview of the information contained in the graph.
Problem 29b
Skin cancer carries a lifetime risk nearly equal to that of all other cancers combined. Following is a graph [modified from K. H. Kraemer (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 94:11 14] depicting the age of onset of skin cancers in patients with or without XP, where the cumulative percentage of skin cancer is plotted against age. The non-XP curve is based on 29,757 cancers surveyed by the National Cancer Institute, and the curve representing those with XP is based on 63 skin cancers from the Xeroderma Pigmentosum Registry.
Explain why individuals with XP show such an early age of onset.
Problem 30
It has been noted that most transposons in humans and other organisms are located in noncoding regions of the genome—regions such as introns, pseudogenes, and stretches of particular types of repetitive DNA. There are several ways to interpret this observation. Describe two possible interpretations. Which interpretation do you favor? Why?
Problem 31a
Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause approximately 30 percent of severe combined immunodeficiency disorder (SCID) cases in humans. These mutations result in alterations to a protein component of cytokine receptors that are essential for proper development of the immune system. The IL2RG gene is composed of eight exons and contains upstream and downstream sequences that are necessary for proper transcription and translation. Below are some of the mutations observed. For each, explain its likely influence on the IL2RG gene product (assume its length to be 375 amino acids).
Nonsense mutation in a coding region
Problem 31b
Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause approximately 30 percent of severe combined immunodeficiency disorder (SCID) cases in humans. These mutations result in alterations to a protein component of cytokine receptors that are essential for proper development of the immune system. The IL2RG gene is composed of eight exons and contains upstream and downstream sequences that are necessary for proper transcription and translation. Below are some of the mutations observed. For each, explain its likely influence on the IL2RG gene product (assume its length to be 375 amino acids).
Insertion in Exon 1, causing frameshift
Problem 31c
Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause approximately 30 percent of severe combined immunodeficiency disorder (SCID) cases in humans. These mutations result in alterations to a protein component of cytokine receptors that are essential for proper development of the immune system. The IL2RG gene is composed of eight exons and contains upstream and downstream sequences that are necessary for proper transcription and translation. Below are some of the mutations observed. For each, explain its likely influence on the IL2RG gene product (assume its length to be 375 amino acids).
Insertion in Exon 7, causing frameshift
Problem 31d
Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause approximately 30 percent of severe combined immunodeficiency disorder (SCID) cases in humans. These mutations result in alterations to a protein component of cytokine receptors that are essential for proper development of the immune system. The IL2RG gene is composed of eight exons and contains upstream and downstream sequences that are necessary for proper transcription and translation. Below are some of the mutations observed. For each, explain its likely influence on the IL2RG gene product (assume its length to be 375 amino acids).
Missense mutation
Problem 31e
Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause approximately 30 percent of severe combined immunodeficiency disorder (SCID) cases in humans. These mutations result in alterations to a protein component of cytokine receptors that are essential for proper development of the immune system. The IL2RG gene is composed of eight exons and contains upstream and downstream sequences that are necessary for proper transcription and translation. Below are some of the mutations observed. For each, explain its likely influence on the IL2RG gene product (assume its length to be 375 amino acids).
Deletion in Exon 2, causing frameshift
Problem 31f
Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause approximately 30 percent of severe combined immunodeficiency disorder (SCID) cases in humans. These mutations result in alterations to a protein component of cytokine receptors that are essential for proper development of the immune system. The IL2RG gene is composed of eight exons and contains upstream and downstream sequences that are necessary for proper transcription and translation. Below are some of the mutations observed. For each, explain its likely influence on the IL2RG gene product (assume its length to be 375 amino acids).
Deletion in Exon 2, in frame
Problem 31g
Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause approximately 30 percent of severe combined immunodeficiency disorder (SCID) cases in humans. These mutations result in alterations to a protein component of cytokine receptors that are essential for proper development of the immune system. The IL2RG gene is composed of eight exons and contains upstream and downstream sequences that are necessary for proper transcription and translation. Below are some of the mutations observed. For each, explain its likely influence on the IL2RG gene product (assume its length to be 375 amino acids).
Large deletion covering Exons 2 and 3
- When a double-strand DNA break occurs in a eukaryotic cell, it may be repaired by either nonhomologous end joining or homologous recombination. How do these different repair mechanisms lead to potentially different outcomes?
Problem 32