Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Struggling with Genetics?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
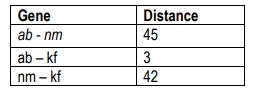
The genetic distances between three genes (ab, nm, kf) were determined using a two-point mapping cross. Determine the sequence of the three genes.
A
Ab – nm – kf
B
Ab – kf – nm
C
Kf – ab – nm
0 Comments
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine the genetic distances provided in the table: ab-nm is 45, ab-kf is 3, and nm-kf is 42.
Understand that the genetic distance is a measure of how far apart genes are on a chromosome, with larger numbers indicating greater distances.
To determine the sequence of genes, consider the smallest distance first, which is ab-kf (3). This suggests that ab and kf are closest to each other.
Next, consider the distance between nm and kf (42). Since nm is far from kf, nm is likely on the opposite side of kf compared to ab.
Finally, verify the sequence by checking the distance between ab and nm (45), which supports the sequence ab-kf-nm, as ab and nm are the farthest apart.
Related Videos
Related Practice
Open Question
Based on previous family studies, an autosomal recessive disease with alleles A and a is suspected to be linked to an RFLP marker. The RFLP marker has four alleles, R₁, R₂, R₃, and R₄. The accompanying pedigree shows a three-generation family in which the disease is present. The gel shows the RFLP alleles for each family member directly below the pedigree symbol for that person. After determining the genotypes for the RFLP and disease gene for each family member, answer the following questions.Based on your analysis, what is the recombination frequency in this family? Explain how you obtained your answer.




