A sample of gas has an initial volume of 14.1 L at a pressure of 1.05 atm. If the sample is compressed to a volume of 10.1 L (at constant temperature), what is its pressure?
Ch.6 - Gases

Chapter 6, Problem 37
A balloon contains 0.119 mol of gas and has a volume of 3.21 L. If an additional 0.103 mol of gas is added to the balloon (at constant temperature and pressure), what is its final volume?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the initial conditions: 0.119 mol of gas with a volume of 3.21 L.
Recognize that the problem involves the ideal gas law, where volume is directly proportional to the number of moles at constant temperature and pressure.
Calculate the total number of moles after adding the additional gas: 0.119 mol + 0.103 mol.
Set up the proportion using the initial and final conditions: \( \frac{V_1}{n_1} = \frac{V_2}{n_2} \), where \( V_1 = 3.21 \text{ L} \), \( n_1 = 0.119 \text{ mol} \), and \( n_2 \) is the total moles after addition.
Solve for \( V_2 \) to find the final volume of the balloon.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation in chemistry that relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature. This law allows us to predict how changes in the amount of gas will affect its volume when temperature and pressure are held constant.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ideal Gas Law Formula
Avogadro's Law
Avogadro's Law states that at constant temperature and pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas present. This means that if you add more moles of gas to a container, the volume will increase proportionally, assuming the temperature and pressure remain unchanged. This principle is crucial for solving problems involving changes in gas quantities.
Recommended video:
Guided course
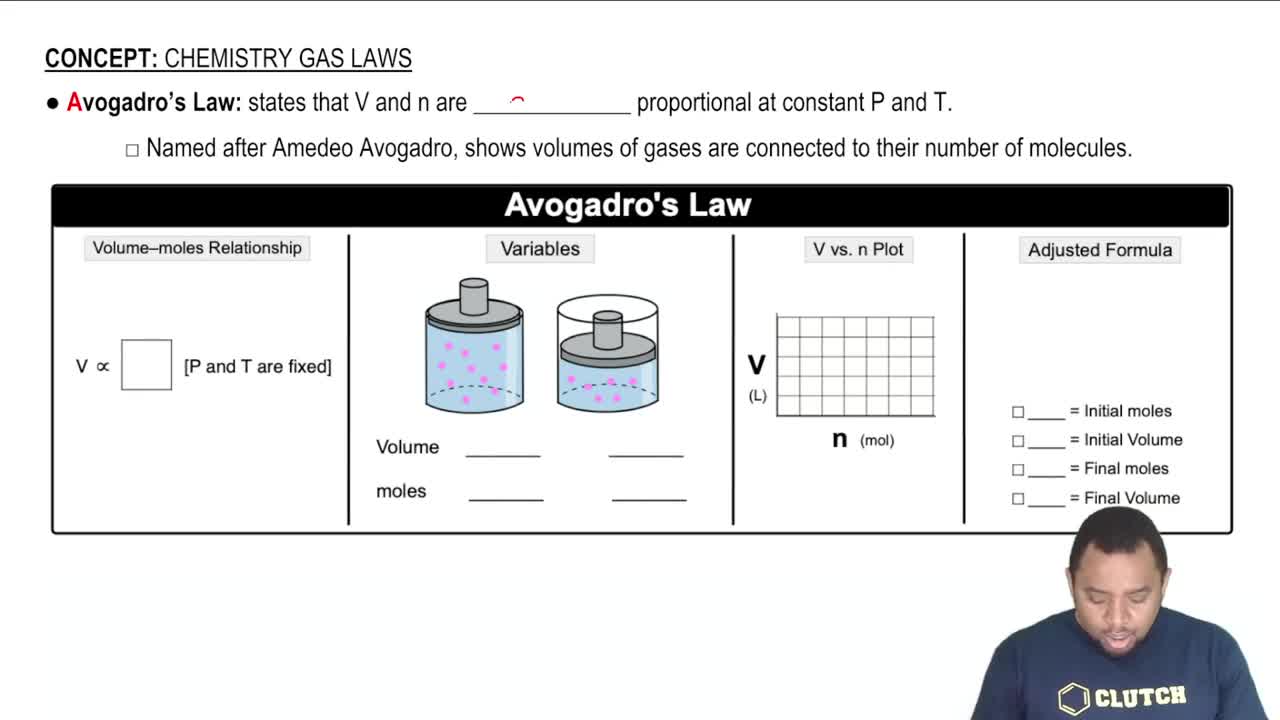
Avogadro's Law
Conservation of Volume in Gases
The conservation of volume in gases refers to the principle that, under constant temperature and pressure, the total volume of a gas mixture is the sum of the volumes of the individual gases. When additional gas is added to a balloon, the total volume can be calculated by adding the initial volume to the volume that corresponds to the added moles of gas, based on the Ideal Gas Law or Avogadro's Law.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Law of Conservation of Mass
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A 48.3-mL sample of gas in a cylinder is warmed from 22 °C to 87 °C. What is its volume at the final temperature?
1
views
Textbook Question
A syringe containing 1.55 mL of oxygen gas is cooled from 95.3 °C to 0.0 °C. What is the final volume of oxygen gas?
2
views
Textbook Question
A cylinder with a moveable piston contains 0.221 mol of gas and has a volume of 178 mL. What is its volume if an additional 0.244 mol of gas is added to the cylinder? (Assume constant temperature and pressure.)
Textbook Question
What volume is occupied by 0.118 mol of helium gas at a pressure of 0.97 atm and a temperature of 305 K?
Textbook Question
What volume is occupied by 0.118 mol of helium gas at a pressure of 0.97 atm and a temperature of 305 K? Would the volume be different if the gas was argon (under the same conditions)?
1
views
