Textbook Question
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. H2C=CH−CH3 b. H3C−CH2−CH3 c. HC≡C−CH3 d. H3C−CH2−CH2−CH3

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance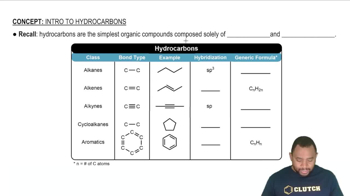
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. H2C=CH−CH3 b. H3C−CH2−CH3 c. HC≡C−CH3 d. H3C−CH2−CH2−CH3
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. HC≡CH
How many molecules of ethanol (C2H5OH) (the alcohol in alcoholic beverages) are present in 145 mL of ethanol? The density of ethanol is 0.789 g/cm3.
A drop of water has a volume of approximately 0.05 mL. How many water molecules does it contain? The density of water is 1.0 g/cm3.