Epsom salts is a hydrated ionic compound with the following formula: MgSO4 • x H2O. A 4.93-g sample of Epsom salts is heated to drive off the water of hydration. The mass of the sample after complete dehydration is 2.41 g. Find the number of waters of hydration (x) in Epsom salts.
Ch.3 - Molecules and Compounds

Chapter 3, Problem 128
Fructose is a common sugar found in fruit. Elemental analysis of fructose gives the following mass percent composition: C 40.00%, H 6.72%, O 53.28%. The molar mass of fructose is 180.16 g/mol. Find the molecular formula of fructose.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1: Assume you have 100 grams of fructose. This allows you to directly convert the mass percentages into grams: 40.00 g of C, 6.72 g of H, and 53.28 g of O.
insert step 2: Convert the masses of each element to moles by dividing by their respective atomic masses: C (12.01 g/mol), H (1.008 g/mol), and O (16.00 g/mol).
insert step 3: Determine the simplest whole number ratio of moles of each element by dividing each by the smallest number of moles calculated in the previous step.
insert step 4: Use the simplest whole number ratio to write the empirical formula of fructose.
insert step 5: Calculate the empirical formula mass and divide the given molar mass of fructose (180.16 g/mol) by the empirical formula mass to find the ratio. Multiply the subscripts in the empirical formula by this ratio to find the molecular formula.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Empirical Formula
The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements in a compound. To determine the empirical formula from mass percent composition, the mass percentages are converted to moles by dividing by the atomic masses of the elements. The resulting mole ratios are then simplified to the smallest whole numbers, providing a foundational understanding of the compound's composition.
Recommended video:
Guided course
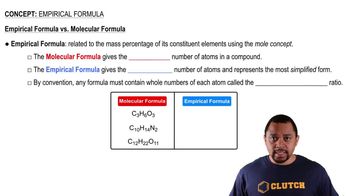
Empirical vs Molecular Formula
Molar Mass
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all atoms in the molecular formula. Knowing the molar mass is crucial for converting between grams and moles, and it helps in determining the molecular formula when combined with the empirical formula.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molar Mass Concept
Molecular Formula
The molecular formula indicates the actual number of each type of atom in a molecule of a compound. It can be derived from the empirical formula by multiplying the subscripts by a whole number, which is determined by dividing the molar mass of the compound by the molar mass of the empirical formula. This formula provides more detailed information about the compound's structure and composition.
Recommended video:
Guided course
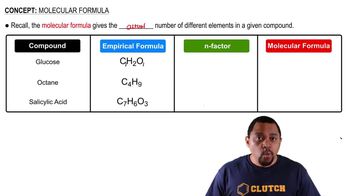
Determining Molecular Formulas
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
A metal (M) forms a compound with the formula MCl3. If the compound contains 65.57% Cl by mass, what is the identity of the metal?
2
views
Textbook Question
A metal (M) forms an oxide with the formula M2O. If the oxide contains 16.99% O by mass, what is the identity of the metal?
2
views
Textbook Question
Combustion analysis of a 13.42-g sample of equilin (which contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) produces 39.61 g CO2 and 9.01 g H2O. The molar mass of equilin is 268.34 g/mol. Find its molecular formula.
1
views
Textbook Question
Estrone, which contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, is a female sexual hormone in the urine of pregnant women. Combustion analysis of a 1.893-g sample of estrone produces 5.545 g of CO2 and 1.388 g H2O. The molar mass of estrone is 270.36 g/mol. Find its molecular formula.
1
views
