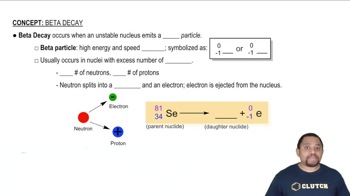
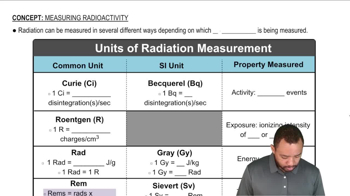
Textbook Question
Complete each nuclear equation and calculate the energy change (in J/mol of reactant) associated with each (Be-9 = 9.012182 amu, Bi-209 = 208.980384 amu, He-4 = 4.002603 amu, Li-6 = 6.015122 amu, Ni-64 = 63.927969 amu, Rg-272 = 272.1535 amu, Ta-179 = 178.94593 amu, and W-179 = 178.94707 amu). a. _____ + 94Be → 63Li + 42He