Textbook Question
Write the nuclear equation for the fusion of two H-2 atoms to form He-3 and one neutron.
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance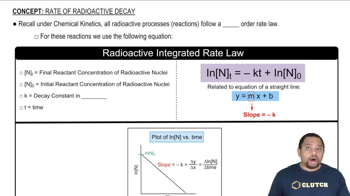

Write the nuclear equation for the fusion of two H-2 atoms to form He-3 and one neutron.
A mammoth skeleton has a carbon-14 decay rate of 0.48 disintegration per minute per gram of carbon (0.48 dis/min • g C). When did the mammoth live? (Assume that living organisms have a carbon-14 decay rate of 15.3 dis/min • g C and that carbon- 14 has a half-life of 5715 yr.)
Write the nuclear reaction for the neutron-induced fission of U-235 to form Xe-144 and Sr-90. How many neutrons are produced in the reaction?
Write the nuclear reaction for the neutron-induced fission of U-235 to produce Te-137 and Zr-97. How many neutrons are produced in the reaction?