Silicon has three naturally occurring isotopes (Si-28, Si-29, and Si-30). The mass and natural abundance of Si-28 are 27.9769 amu and 92.2%, respectively. The mass and natural abundance of Si-29 are 28.9765 amu and 4.67%, respectively. Find the mass and natural abundance of Si-30.
Ch.2 - Atoms & Elements

Chapter 2, Problem 87
Use the mass spectrum of europium to determine the atomic mass of europium.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the isotopes of europium present in the mass spectrum and their respective abundances.
List the isotopic masses of each europium isotope. These are typically given in atomic mass units (amu).
For each isotope, multiply the isotopic mass by its relative abundance (expressed as a decimal).
Sum the products from the previous step to obtain the weighted average atomic mass of europium.
Ensure the final atomic mass is expressed in atomic mass units (amu) and reflects the weighted average of all isotopes present.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mass Spectrum
A mass spectrum is a graphical representation of the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It provides information about the different isotopes of an element and their relative abundances. In the case of europium, the mass spectrum will show peaks corresponding to its isotopes, allowing for the calculation of the average atomic mass based on their relative intensities.
Recommended video:
Guided course
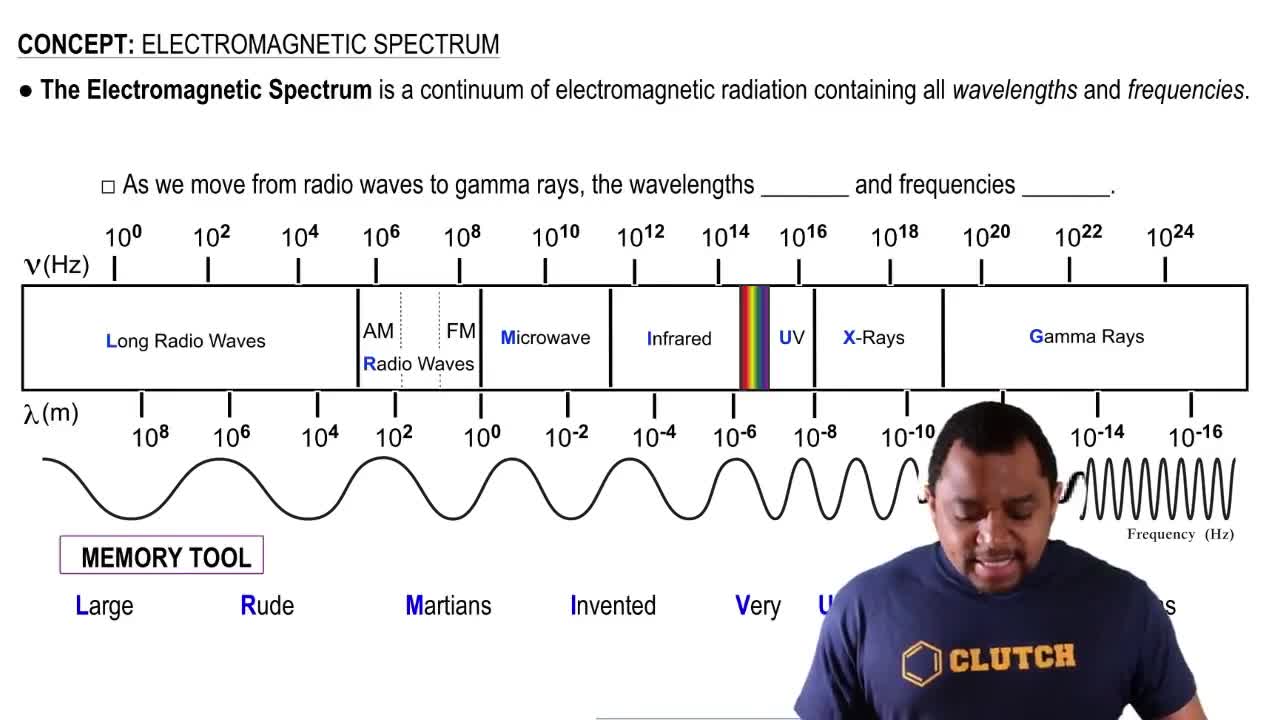
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Isotopes
Isotopes are variants of a chemical element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses. For europium, the most common isotopes are europium-151 and europium-153. Understanding isotopes is crucial for accurately determining the atomic mass, as the average atomic mass is a weighted average based on the abundance of each isotope.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isotopes
Atomic Mass Calculation
The atomic mass of an element is calculated by taking the weighted average of the masses of its isotopes, considering their relative abundances. This involves multiplying the mass of each isotope by its fractional abundance and summing these values. For europium, this calculation will yield a precise atomic mass that reflects the contributions of its isotopes as observed in the mass spectrum.
Recommended video:
Guided course
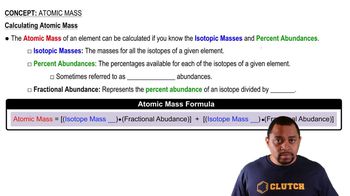
Calculating Atomic Mass
Related Practice
Textbook Question
3
views
Textbook Question
An element has four naturally occurring isotopes with the masses and natural abundances given here. Find the atomic mass of the element and identify it.
Isotope Mass (amu) Abundance (%)
1 135.90714 0.19
2 137.90599 0.25
3 139.90543 88.43
4 141.90924 11.13
Textbook Question
Bromine has two naturally occurring isotopes (Br-79 and Br-81) and has an atomic mass of 79.904 amu. The mass of Br-81 is 80.9163 amu, and its natural abundance is 49.31%. Calculate the mass and natural abundance of Br-79.
4
views
Textbook Question
Use the mass spectrum of rubidium to determine the atomic mass of rubidium.
Textbook Question
How many sulfur atoms are there in 5.52 mol of sulfur?
1
views
Textbook Question
A gold sample contains 4.65×1024 gold atoms. How many moles of gold does the sample contain?
