Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. b. pH = 7
Ch.18 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium

Chapter 18, Problem 105c
Determine if each compound is more soluble in acidic solution than it is in pure water. Explain. a. BaCO3 b. CuS c. AgCl d. PbI2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the compound in question: AgCl (Silver Chloride).
Recall the solubility product constant (Ksp) for AgCl, which is a measure of its solubility in water.
Consider the dissolution reaction of AgCl in water: \[ \text{AgCl(s)} \rightleftharpoons \text{Ag}^+(aq) + \text{Cl}^-(aq) \]
Determine if the anion (Cl⁻) can react with H⁺ ions in an acidic solution. Since Cl⁻ is the conjugate base of a strong acid (HCl), it does not react with H⁺ ions.
Conclude that since Cl⁻ does not react with H⁺, the solubility of AgCl is not increased in an acidic solution compared to pure water.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that applies to the solubility of sparingly soluble ionic compounds. It quantifies the extent to which a compound can dissolve in water, represented by the product of the molar concentrations of its ions, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced equation. For AgCl, Ksp helps determine how its solubility changes in different conditions, such as acidic solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solubility Product Constant
Common Ion Effect
The common ion effect refers to the decrease in solubility of an ionic compound when a common ion is added to the solution. In the case of AgCl, the presence of Ag+ ions from another source can shift the dissolution equilibrium, reducing the solubility of AgCl. Understanding this effect is crucial for predicting how the solubility of AgCl will change in acidic solutions where other ions may be present.
Recommended video:
Guided course
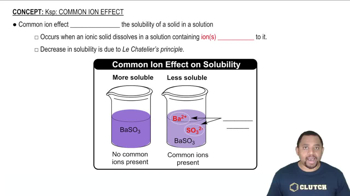
Common Ion Effect
Acid-Base Chemistry
Acid-base chemistry involves the study of proton transfer reactions and the behavior of acids and bases in solution. In acidic solutions, the concentration of H+ ions increases, which can affect the solubility of certain salts. For AgCl, the addition of H+ ions can lead to the formation of soluble complexes, potentially increasing its solubility compared to pure water, making it essential to consider acid-base interactions when analyzing solubility.
Recommended video:
Guided course
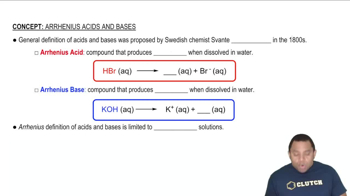
Arrhenius Acids and Bases
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. c. pH = 9
Textbook Question
Calculate the solubility (in grams per 1.00⨉102 mL of solution) of magnesium hydroxide in a solution buffered at pH = 10. How does this compare to the solubility of Mg(OH)2 in pure water?
Textbook Question
A solution containing sodium fluoride is mixed with one containing calcium nitrate to form a solution that is 0.015 M in NaF and 0.010 M in Ca(NO3)2. Does a precipitate form in the mixed solution? If so, identify the precipitate.
Textbook Question
Predict whether a precipitate will form if you mix 75.0 mL of a NaOH solution with pOH = 2.58 with 125.0 mL of a 0.018 M MgCl2 solution. Identify the precipitate, if any.
