Textbook Question
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. a. pH = 4
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

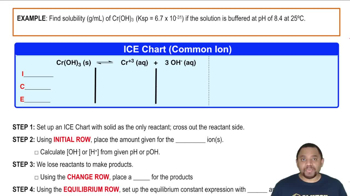
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. a. pH = 4
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. b. pH = 7
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. c. pH = 9
Determine if each compound is more soluble in acidic solution than it is in pure water. Explain. a. BaCO3 b. CuS c. AgCl d. PbI2
A solution containing sodium fluoride is mixed with one containing calcium nitrate to form a solution that is 0.015 M in NaF and 0.010 M in Ca(NO3)2. Does a precipitate form in the mixed solution? If so, identify the precipitate.