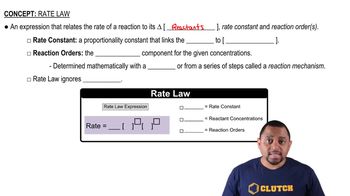
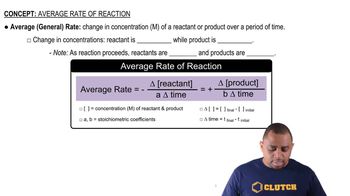
Consider the reaction: H2( g) + Br2( g) → 2 HBr( g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time.
b. Make a rough sketch of a curve representing the concentration of HBr as a function of time. Assume that the initial concentration of HBr is zero