Textbook Question
Explain the observed trend in the melting points of the hydrogen halides.
HI -50.8 °C
HBr -88.5 °C
HCl -114.8 °C
HF -83.1 °C
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
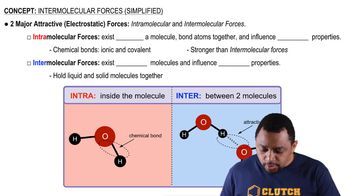
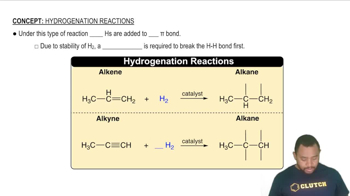

Explain the observed trend in the melting points of the hydrogen halides.
HI -50.8 °C
HBr -88.5 °C
HCl -114.8 °C
HF -83.1 °C
The vapor pressure of water at 25 °C is 23.76 torr. If 0.25 g of water is enclosed in a 1.50-L container, will any liquid be present? If so, what mass of liquid?
The vapor pressure of CCl3F at 300 K is 856 torr. If 3.5 g of CCl3F is enclosed in a 1.0-L container, will any liquid be present? If so, what mass of liquid?