Ch.4 - Atoms and Elements

Chapter 3, Problem 32
Sulfuric acid dissolves aluminum metal according to the reaction:
2 Al(s) + 3 H2SO4(aq) → Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3 H2( g)
Suppose you want to dissolve an aluminum block with a mass of 15.2 g. What minimum mass of H2SO4 (in g) do you need? What mass of H2 gas (in g) does the complete reaction of the aluminum block produce?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Calculate the moles of aluminum (Al) using its molar mass.
Use the stoichiometry of the balanced chemical equation to determine the moles of H2SO4 needed.
Convert the moles of H2SO4 to grams using its molar mass.
Use the stoichiometry of the balanced chemical equation to determine the moles of H2 gas produced.
Convert the moles of H2 gas to grams using its molar mass.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions based on the balanced chemical equation. It allows us to determine the proportions of substances involved in a reaction. In this case, the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced equation indicate the molar ratios of aluminum to sulfuric acid and hydrogen gas, which are essential for calculating the required mass of sulfuric acid and the mass of hydrogen produced.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Molar Mass
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It is crucial for converting between the mass of a substance and the number of moles, which is necessary for stoichiometric calculations. For aluminum (Al) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4), knowing their molar masses allows us to calculate how much sulfuric acid is needed to react with a given mass of aluminum.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molar Mass Concept
Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases under various conditions of temperature and pressure. In this context, the production of hydrogen gas (H2) from the reaction can be quantified using the ideal gas law if needed. Understanding gas laws helps in predicting the volume or mass of gas produced in a reaction, which is important for determining the amount of hydrogen generated from the complete reaction of aluminum.
Recommended video:
Guided course
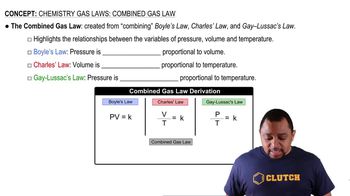
Combined Gas Law
0
