Textbook Question
Calculate the molarity of each solution.
a. 3.25 mol of LiCl in 2.78 L solution
b. 28.33 g C6H12O6 in 1.28 L of solution

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


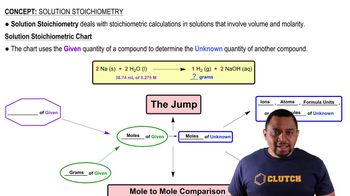
Calculate the molarity of each solution.
a. 3.25 mol of LiCl in 2.78 L solution
b. 28.33 g C6H12O6 in 1.28 L of solution
Calculate the molarity of each solution.
c. 32.4 mg NaCl in 122.4 mL of solution
What is the molarity of Cl- in each solution? b. 0.150 M SrCl2
what is the molarity of Cl- in each solution? c. 0.100 M AlCl3
How many moles of KCl are contained in each solution? a. 0.556 L of a 2.3 M KCl solution