In analytical chemistry, bases used for titrations must often be standardized; that is, their concentration must be precisely determined. Standardization of sodium hydroxide solutions can be accomplished by titrating potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H4O4), also known as KHP, with the NaOH solution to be standardized. b. The titration of 0.5527 g of KHP required 25.87 mL of an NaOH solution to reach the equivalence point. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution?
Ch.18 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium

Chapter 18, Problem 123
From the data given—where a 0.552-g sample of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is dissolved in water to a total volume of 20.0 mL and titrated with 0.1103 M KOH, the equivalence point occurred at 28.42 mL, and the pH of the solution at 10.0 mL of added base was 3.72—determine the molar mass and dissociation constant (Ka) for vitamin C.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Calculate the moles of KOH at the equivalence point using the volume and molarity of KOH: \( \text{moles of KOH} = M \times V \).
Since the moles of KOH equal the moles of ascorbic acid at the equivalence point, use this to find the moles of ascorbic acid.
Determine the molar mass of ascorbic acid by dividing the mass of the sample by the moles of ascorbic acid: \( \text{Molar mass} = \frac{\text{mass}}{\text{moles}} \).
Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to find the pKa at the point where 10.0 mL of KOH is added: \( \text{pH} = \text{pKa} + \log\left(\frac{[\text{A}^-]}{[\text{HA}]}\right) \).
Calculate the dissociation constant \( K_a \) from the pKa using the relation \( K_a = 10^{-\text{pKa}} \).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molar Mass Calculation
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). To calculate the molar mass of ascorbic acid in this scenario, you can use the mass of the sample and the number of moles of KOH used at the equivalence point. The relationship between moles, mass, and molar mass is given by the formula: Molar Mass = Mass / Moles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molar Mass Calculation Example
Titration and Equivalence Point
Titration is a quantitative analytical method used to determine the concentration of a solute in a solution. The equivalence point is reached when the amount of titrant added is stoichiometrically equivalent to the amount of analyte in the solution. In this case, the volume of KOH at the equivalence point allows for the calculation of moles of ascorbic acid, which is essential for determining its molar mass.
Recommended video:
Guided course
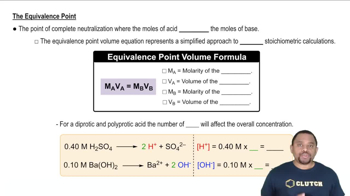
Equivalence Point in Titration
Dissociation Constant (Ka)
The dissociation constant (Ka) is a measure of the strength of an acid in solution, indicating how well it donates protons (H+) to the solution. For weak acids like ascorbic acid, Ka can be calculated using the concentrations of the products and reactants at equilibrium. In this case, the pH at a specific volume of KOH added can be used to find the concentration of H+ ions, which is necessary for calculating Ka.
Recommended video:
Guided course
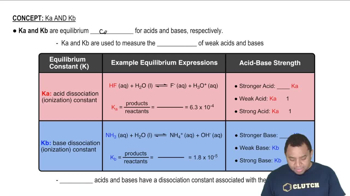
Characteristics of Ka and Kb
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A 5.55-g sample of a weak acid with Ka = 1.3⨉10-4 was combined with 5.00 mL of 6.00 M NaOH, and the resulting solution was diluted to 750.0 mL. The measured pH of the solution was 4.25. What is the molar mass of the weak acid?
Textbook Question
Pseudogout, a condition with symptoms similar to those of gout (see Problem 126), is caused by the formation of calcium diphosphate (Ca2P2O7) crystals within tendons, cartilage, and ligaments. Calcium diphosphate will precipitate out of blood plasma when diphosphate levels become abnormally high. If the calcium concentration in blood plasma is 9.2 mg/dL, and Ksp for calcium diphosphate is 8.64⨉10-13, what minimum concentration of diphosphate results in precipitation?
