Morphine has the formula C17H19NO3. It is a base and accepts one proton per molecule. It is isolated from opium. A 0.682-g sample of opium is found to require 8.92 mL of a 0.0116 M solution of sulfuric acid for neutralization. Assuming that morphine is the only acid or base present in opium, calculate the percent morphine in the sample of opium.
Ch.17 - Acids and Bases

Chapter 17, Problem 139
Determine the pH of each two-component solution. a. 0.0550 M in HI and 0.00850 M in HF b. 0.112 M in NaCl and 0.0953 M in KF c. 0.132 M in NH4Cl and 0.150 M HNO3 d. 0.0887 M in sodium benzoate and 0.225 M in potassium bromide e. 0.0450 M in HCl and 0.0225 M in HNO3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the nature of each component in the solution. For example, HI is a strong acid, HF is a weak acid, NaCl is a neutral salt, KF is a salt that can affect pH due to the F- ion, NH4Cl is an acidic salt, HNO3 is a strong acid, sodium benzoate is a salt of a weak acid, and potassium bromide is a neutral salt.
Step 2: For solutions containing strong acids (like HI and HCl), calculate the pH directly from the concentration of the strong acid, as they dissociate completely in water. Use the formula: \( \text{pH} = -\log[\text{H}^+] \).
Step 3: For solutions containing weak acids (like HF), use the acid dissociation constant (Ka) to find the concentration of \( \text{H}^+ \) ions. Set up an equilibrium expression: \( \text{HF} \rightleftharpoons \text{H}^+ + \text{F}^- \) and solve for \( \text{H}^+ \) using the equation \( K_a = \frac{[\text{H}^+][\text{F}^-]}{[\text{HF}]} \).
Step 4: For solutions containing salts that can affect pH (like KF or NH4Cl), determine if the salt will hydrolyze in water. For KF, the F- ion can react with water to form HF and OH-, making the solution basic. For NH4Cl, the NH4+ ion can donate a proton to water, making the solution acidic.
Step 5: For mixtures of strong acids (like HCl and HNO3), add the concentrations of \( \text{H}^+ \) ions from each acid to find the total \( \text{H}^+ \) concentration, then calculate the pH using \( \text{pH} = -\log[\text{H}^+] \).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
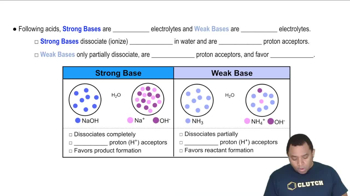
Strong vs. Weak Acids and Bases
Understanding the difference between strong and weak acids and bases is crucial for pH calculations. Strong acids, like HI and HCl, completely dissociate in solution, contributing to a higher concentration of hydrogen ions (H+). In contrast, weak acids, such as HF, only partially dissociate, resulting in a lower concentration of H+. This distinction affects the overall pH of the solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Strong vs Weak Bases
pH Calculation
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, calculated using the formula pH = -log[H+]. For strong acids, the pH can be directly derived from their molarity, while for weak acids, the dissociation constant (Ka) must be used to find the equilibrium concentration of H+. This calculation is essential for determining the pH of the given solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

pH Calculation Example
Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acids or bases. They typically consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. In the context of the question, solutions containing components like sodium benzoate and potassium bromide may act as buffers, influencing the pH in a way that requires consideration of both components' contributions to the overall acidity or basicity.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Buffer Solutions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The AIDS drug zalcitabine (also known as ddC) is a weak base with a pKb of 9.8. What percentage of the base is protonated in an aqueous zalcitabine solution containing 565 mg/L?
Textbook Question
Determine the pH of each two-component solution. d. 0.088 M HClO4 and 0.022 M KOH
Textbook Question
Write net ionic equations for the reactions that take place when aqueous solutions of the following substances are mixed: a. sodium cyanide and nitric acid b. ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide c. sodium cyanide and ammonium bromide d. potassium hydrogen sulfate and lithium acetate e. sodium hypochlorite and ammonia
