Textbook Question
Determine the pH of each solution. a. 0.10 M NH4Cl

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
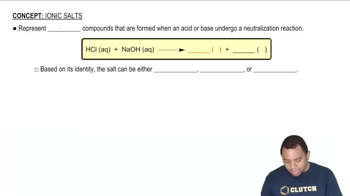
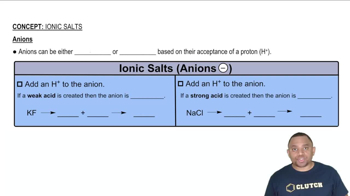

Determine the pH of each solution. a. 0.10 M NH4Cl
Determine whether each cation is acidic or pH-neutral. For each cation that is acidic, write an equation that shows how the cation acts as an acid. d. Li+
Determine if each salt will form a solution that is acidic, basic, or pH-neutral. e. C6H5NH3NO2
Arrange the solutions in order of increasing acidity. NaCl, NH4Cl, NaHCO3, NH4ClO2, NaOH