Textbook Question
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of aqueous potassium hydroxide with aqueous iron(III) chloride to form solid iron(III) hydroxide and aqueous potassium chloride.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance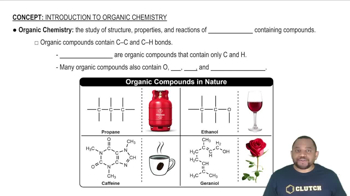

Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of aqueous potassium hydroxide with aqueous iron(III) chloride to form solid iron(III) hydroxide and aqueous potassium chloride.
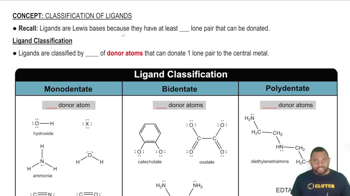
Balance each chemical equation. b. Co(NO3)3(aq) + (NH4)2S(aq) → Co2S3(s) + NH4NO3(aq)
Balance each chemical equation. a. Na2S(aq) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) → NaNO3(aq) + CuS(s) b. N2H4(l) → NH3(g) + N2(g) c. HCl(aq) + O2(g) → H2O(l) + Cl2(g) d. FeS(s) + HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g)
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. H2C=CH−CH3 b. H3C−CH2−CH3 c. HC≡C−CH3 d. H3C−CH2−CH2−CH3
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. HC≡CH