Which metal can be oxidized with an Sn2+ solution but not with an Fe2+ solution?

Determine whether or not each metal dissolves in 1 M HNO3. For those metals that do dissolve, write a balanced redox reaction showing what happens when the metal dissolves. a. Cu b. Au
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
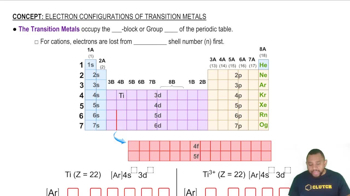
Key Concepts
Redox Reactions
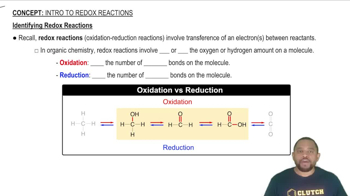
Metal Reactivity
Balanced Chemical Equations

Determine whether or not each metal dissolves in 1 M HCl. For those metals that do dissolve, write a balanced redox reaction showing what happens when the metal dissolves. a. Al b. Ag c. Pb
Determine whether or not each metal dissolves in 1 M HCl. For those metals that do dissolve, write a balanced redox reaction showing what happens when the metal dissolves. a. Cu b. Fe c. Au
Determine whether or not each metal dissolves in 1 M HIO3. For those metals that do dissolve, write a balanced redox equation for the reaction that occurs. a. Au b. Cr
Calculate E°cell for each balanced redox reaction and determine if the reaction is spontaneous as written. a. 2 Cu(s) + Mn2+(aq) → 2 Cu+(aq) + Mn(s)
Calculate E°cell for each balanced redox reaction and determine if the reaction is spontaneous as written. b. MnO2(aq) + 4 H+(aq) + Zn(s) → Mn2+(aq) + 2H2O(l) + Zn2+(aq) c. Cl2(g) + 2 F–(aq) → F2(g) + 2 Cl–(aq)
