Textbook Question
Determine the sign of ΔSsys for each process. a. water boiling

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


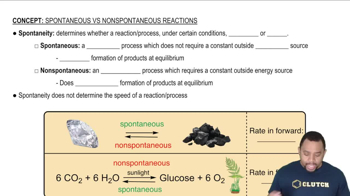
Determine the sign of ΔSsys for each process. a. water boiling
Determine the sign of ΔSsys for each process. b. water freezing
Consider this reaction occurring at 298 K: N2O(g) + NO2(g) ⇌ 3 NO(g) a. Show that the reaction is not spontaneous under standard conditions by calculating ΔG°rxn.