Textbook Question
In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. b. CH3NH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3NH3+(aq) + OH–(aq)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
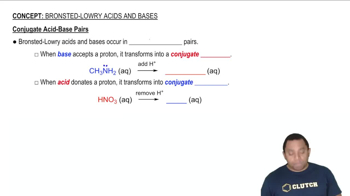

In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. b. CH3NH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3NH3+(aq) + OH–(aq)
In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. c. CO32–(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCO3–(aq) + OH–(aq)
Write the formula for the conjugate base of each acid. a. HCl
Write the formula for the conjugate base of each acid. c. HCHO2
Write the formula for the conjugate base of each acid. d. HF
Write the formula for the conjugate acid of each base. a. NH3 b. ClO4– c. HSO4– d. CO32–