Textbook Question
Write equations showing how each weak base ionizes water to form OH–. Also write the corresponding expression for Kb. b. C6H5NH2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Write equations showing how each weak base ionizes water to form OH–. Also write the corresponding expression for Kb. b. C6H5NH2
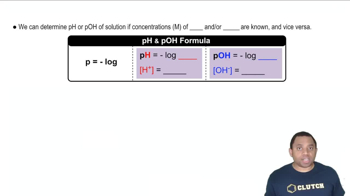
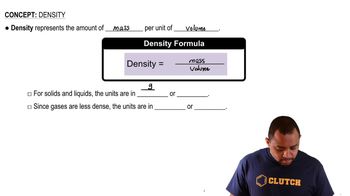
Determine the pH of a solution that is 3.85% KOH by mass. Assume that the solution has density of 1.01 g/mL.
Write equations showing how each weak base ionizes water to form OH–. Also write the corresponding expression for Kb. a. NH3 b. HCO3– c. CH3NH2
Write equations showing how each weak base ionizes water to form OH–. Also write the corresponding expression for Kb. a. CO32–