Consider this overall reaction, which is experimentally observed to be second order in AB and zero order in C: AB + C → A + BC Is the following mechanism valid for this reaction? AB + AB →k1 AB2 + A Slow AB2 + C → k2 AB + BC Fast
Ch.14 - Chemical Kinetics

Chapter 14, Problem 77b
Consider this three-step mechanism for a reaction:
Cl2 (g) k1⇌k2 2 Cl (g) Fast
Cl (g) + CHCl3 (g) →k3 HCl (g) + CCl3 (g) Slow
Cl (g) + CCl3 (g) →k4 CCl4 (g) Fast
b. Identify the intermediates in the mechanism.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Intermediates are species that are produced in one step of a reaction mechanism and consumed in a subsequent step.
Examine each step of the mechanism to identify species that are not present in the overall balanced equation.
In the first step, Cl2 dissociates into 2 Cl atoms.
In the second step, Cl reacts with CHCl3 to form HCl and CCl3.
In the third step, Cl reacts with CCl3 to form CCl4.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Reaction Mechanism
A reaction mechanism is a step-by-step description of how a chemical reaction occurs at the molecular level. It outlines the sequence of elementary steps that lead to the overall reaction, including the formation and consumption of intermediates. Understanding the mechanism helps in predicting the rate and outcome of the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course
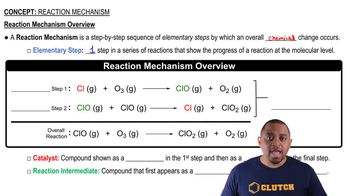
Reaction Mechanism Overview
Intermediates
Intermediates are species that are formed during the reaction mechanism but are not present in the final products. They are typically unstable and exist only for a short duration before being converted into products. Identifying intermediates is crucial for understanding the pathway of the reaction and its kinetics.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Reaction Mechanism Example
Rate-Determining Step
The rate-determining step is the slowest step in a reaction mechanism that controls the overall reaction rate. It is the step that has the highest activation energy and thus takes the longest time to occur. Recognizing the rate-determining step is essential for predicting how changes in conditions will affect the reaction rate.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rate Law Determination
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2
views
Textbook Question
Consider this three-step mechanism for a reaction:
Cl2 (g) k1⇌k2 2 Cl (g) Fast
Cl (g) + CHCl3 (g) →k3 HCl (g) + CCl3 (g) Slow
Cl (g) + CCl3 (g) →k4 CCl4 (g) Fast
a. What is the overall reaction?
Textbook Question
Consider this three-step mechanism for a reaction:
Cl2 (g) k1⇌k2 2 Cl (g) Fast
Cl (g) + CHCl3 (g) →k3 HCl (g) + CCl3 (g) Slow
Cl (g) + CCl3 (g) →k4 CCl4 (g) Fast
c. What is the predicted rate law?
1
views
Textbook Question
Consider this two-step mechanism for a reaction: NO2(g) + Cl2(g) → k1 ClNO2(g) + Cl g) Slow NO2(g) + Cl(g) →k2 ClNO2(g) Fast b. Identify the intermediates in the mechanism.
