When HNO2 is dissolved in water, it partially dissociates according to the equation HNO2 ⇌ H+ + NO2-. A solution is prepared that contains 7.050 g of HNO2 in 1.000 kg of water. Its freezing point is -0.2929 °C. Calculate the fraction of HNO2 that has dissociated.
Ch.13 - Solutions

Chapter 13, Problem 116
The density of a 0.438 M solution of potassium chromate (K2CrO4) at 298 K is 1.063 g/mL. Calculate the vapor pressure of water above the solution. The vapor pressure of pure water at this temperature is 0.0313 atm. (Assume complete dissociation of the solute.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Calculate the molality of the solution using the formula: \( \text{molality} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{kilograms of solvent}} \). First, find the moles of K2CrO4 using its molarity and the volume of the solution.
Determine the mass of the solution using its density and volume. Then, calculate the mass of the solvent (water) by subtracting the mass of the solute from the total mass of the solution.
Use the molality to find the change in vapor pressure using Raoult's Law: \( \Delta P = i \cdot X_{\text{solute}} \cdot P^0_{\text{water}} \), where \( i \) is the van't Hoff factor, \( X_{\text{solute}} \) is the mole fraction of the solute, and \( P^0_{\text{water}} \) is the vapor pressure of pure water.
Calculate the mole fraction of the solute, \( X_{\text{solute}} \), using the formula: \( X_{\text{solute}} = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{moles of solute} + \text{moles of solvent}} \).
Subtract the change in vapor pressure, \( \Delta P \), from the vapor pressure of pure water to find the vapor pressure of water above the solution.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
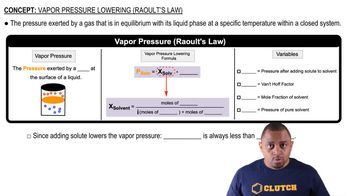
Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase at a given temperature. It reflects the tendency of particles to escape from the liquid phase into the vapor phase. In solutions, the presence of solute particles lowers the vapor pressure compared to that of the pure solvent, a phenomenon described by Raoult's Law.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Raoult's Law and Vapor Pressure
Raoult's Law
Raoult's Law states that the vapor pressure of a solvent in a solution is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent. It can be expressed mathematically as P_solution = X_solvent * P°_solvent, where P_solution is the vapor pressure of the solution, X_solvent is the mole fraction of the solvent, and P°_solvent is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent. This law is crucial for calculating the vapor pressure of solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Raoult's Law and Vapor Pressure
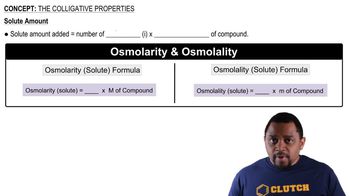
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. These properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. Understanding colligative properties is essential for predicting how solutes affect the physical properties of solvents, such as vapor pressure.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Colligative Properties
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
A solution of a nonvolatile solute in water has a boiling point of 375.3 K. Calculate the vapor pressure of water above this solution at 338 K. The vapor pressure of pure water at this temperature is 0.2467 atm.
3
views
Textbook Question
The vapor pressure of carbon tetrachloride, CCl4, is 0.354 atm, and the vapor pressure of chloroform, CHCl3, is 0.526 atm at 316 K. A solution is prepared from equal masses of these two compounds at this temperature. Calculate the mole fraction of the chloroform in the vapor above the solution. If the vapor above the original solution is condensed and isolated into a separate flask, what will the vapor pressure of chloroform be above this new solution?
