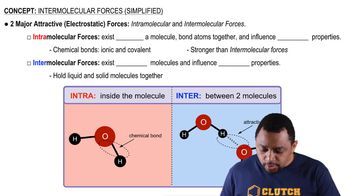
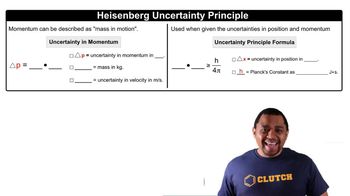
Textbook Question
Pick an appropriate solvent from Table 13.3 to dissolve each substance. State the kind of intermolecular forces that would occur between the solute and solvent in each case. a. isopropyl alcohol (polar, contains an OH group) c. vegetable oil (nonpolar) d. sodium nitrate (ionic)