Textbook Question
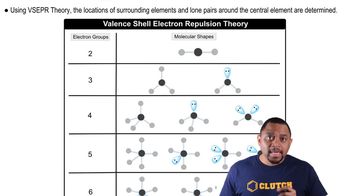
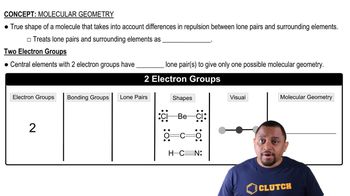
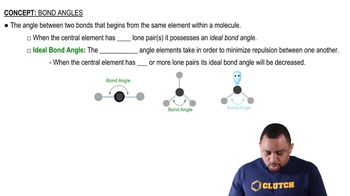
Oceanographers study the mixing of water masses by releasingtracer molecules at a site and then detecting their presence atother places. The molecule trifluoromethylsulfur pentafluorideis one such tracer. Draw an electron-dot structure for CF3SF5,and predict the bond angles around both carbon and sulfur.