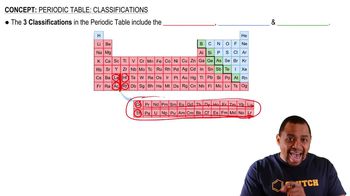
Textbook Question
Phosphorus can have several different oxidation numbers ranging in value from -3 to +5. (a) When phosphorus burns in air or oxygen, it yields either tetraphosphorus hexoxide or tetraphosphorus decoxide. Write the formula and give the oxidation number for each compound.