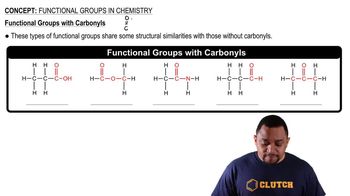
Textbook Question
Methionine, one of the 20 amino acid building blocks from which proteins are made, has the following structure. What is the chemical formula of methionine? In writing the for-mula, list the element symbols in alphabetical order, and give the number of each element as a subscript.