Textbook Question
Convert the following model into a condensed structure and line drawing. Draw the structures of two isomeric compounds.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
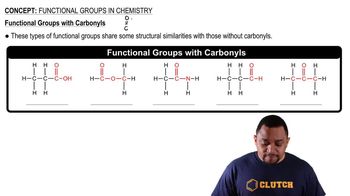
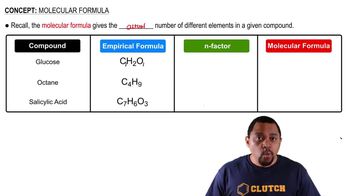
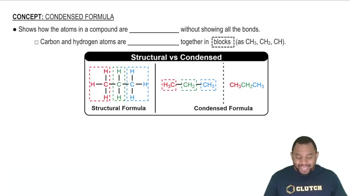
Convert the following model into a condensed structure and line drawing. Draw the structures of two isomeric compounds.
Propose structures and draw condensed formulas for molecules that meet the following descriptions.
(a) A ketone with the formula C5H10
Give line drawings for each of the following molecular formulas. You may have to use rings and/or multiple bonds in some instances.
(a) C2H7N
Propose structures and draw condensed formulas for molecules that meet the following descriptions.
(c) A compound with formula C2H5NO2 that is both an amine and a carboxylic acid