Textbook Question
Propose structures and draw condensed formulas for molecules that meet the following descriptions.
(b) An ester with the formula C6H12O2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance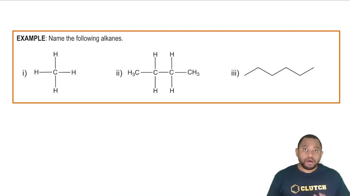
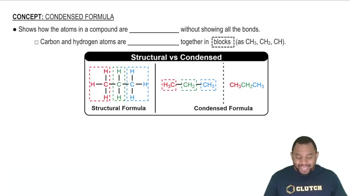
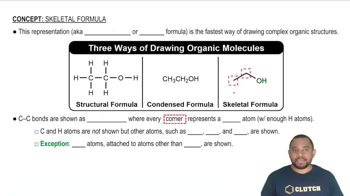
Propose structures and draw condensed formulas for molecules that meet the following descriptions.
(b) An ester with the formula C6H12O2
Propose structures and draw condensed formulas for molecules that meet the following descriptions.
(c) A compound with formula C2H5NO2 that is both an amine and a carboxylic acid