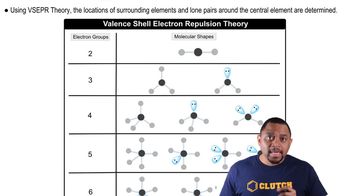
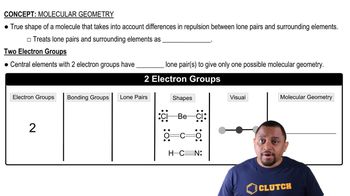
Step 1: Determine the total number of valence electrons for each molecule. For H2S, sulfur (S) has 6 valence electrons and each hydrogen (H) has 1 valence electron, totaling 8 valence electrons. For SO2, sulfur has 6 valence electrons and each oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons, totaling 18 valence electrons. For SO3, sulfur has 6 valence electrons and each oxygen has 6 valence electrons, totaling 24 valence electrons.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance