Ch.22 - The Main Group Elements

Chapter 22, Problem 162
Write balanced equations for the reactions of (a) H3PO4 and (b) B1OH23 with water. Classify each acid as a Brønsted–Lowry acid or a Lewis acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the chemical formulas for the given acids. For (a) H3PO4 is phosphoric acid, and for (b) B1OH23, it seems like a typo or unconventional notation. Assuming it refers to a boron compound, let's consider a typical boron compound like B(OH)3, boric acid.
Step 2: Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of H3PO4 with water. H3PO4 is a Brønsted–Lowry acid, which donates a proton (H+) to water, forming H2PO4- and H3O+.
Step 3: Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of B(OH)3 with water. B(OH)3 acts as a Lewis acid, accepting a pair of electrons from water to form a complex, typically B(OH)4- and H+.
Step 4: Classify each acid. H3PO4 is a Brønsted–Lowry acid because it donates a proton to water. B(OH)3 is a Lewis acid because it accepts an electron pair from water.
Step 5: Review the definitions: A Brønsted–Lowry acid is a substance that donates a proton (H+), while a Lewis acid is a substance that accepts an electron pair.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balanced Chemical Equations
A balanced chemical equation represents a chemical reaction where the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is crucial for obeying the law of conservation of mass. To balance an equation, coefficients are adjusted to ensure that the total number of each type of atom is equal before and after the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Brønsted–Lowry Acids and Bases
The Brønsted–Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. In this context, an acid like H3PO4 donates a proton (H+) to water, forming hydronium ions (H3O+). This classification helps in understanding the behavior of substances in aqueous solutions and their role in acid-base reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Example
Lewis Acids and Bases
The Lewis theory expands the definition of acids and bases beyond protons. A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor, while a Lewis base is an electron pair donor. In the case of B1OH23, if it accepts an electron pair from water, it can be classified as a Lewis acid, illustrating the broader interactions in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
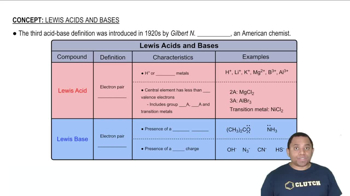
Lewis Acids and Bases
Related Practice
