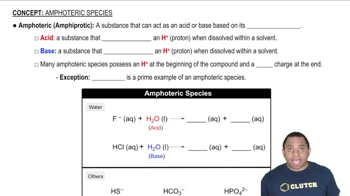
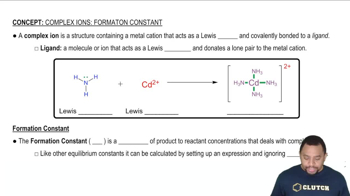
Net Ionic Equations
A net ionic equation represents the chemical species that are actually involved in a reaction, omitting the spectator ions that do not participate. To write a net ionic equation, one must first write the balanced molecular equation, then dissociate the soluble strong electrolytes into their ions, and finally eliminate the spectator ions to focus on the core reaction.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance