Look at the location of elements A, B, C, and D in the following periodic table:
(d) Which hydrides react with water to give an acidic solution, and which give a basic solution?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

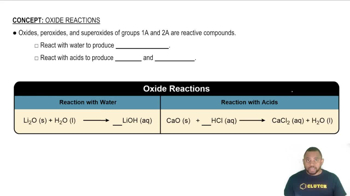
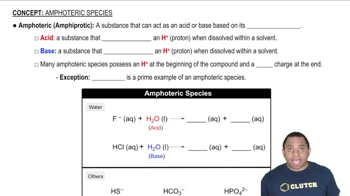
Look at the location of elements A, B, C, and D in the following periodic table:
(d) Which hydrides react with water to give an acidic solution, and which give a basic solution?
Look at the location of elements A, B, C, and D in the following
periodic table:
(c) Which hydrides react with water to give H2 gas? Write a balanced net ionic equation for each reaction.
The following models represent the structures of binary hydrides
of second-row elements:
(a) Identify the nonhydrogen atom in each case, and write the molecular formula for each hydride.
In what forms is oxygen commonly found in nature?
Explain why the properties of boron differ so markedly from the properties of the other group 3A elements.
Describe the structures of the white and red allotropes of phosphorus, and explain why white phosphorus is so reactive.