Ch.22 - The Main Group Elements

Chapter 22, Problem 42
Which of the following compounds are molecular, and which have an extended three-dimensional structure? (a) B2H6 (b) KAlSi3O8 (c) SO3 (d) GeCl4
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the difference between molecular compounds and those with extended three-dimensional structures. Molecular compounds consist of discrete molecules held together by covalent bonds, while compounds with extended structures are typically ionic or covalent networks.
Step 2: Analyze compound (a) B2H6. Diborane (B2H6) is a molecular compound because it consists of discrete B2H6 molecules held together by covalent bonds.
Step 3: Analyze compound (b) KAlSi3O8. This is a mineral known as feldspar, which has an extended three-dimensional structure. It is a network solid with a complex lattice structure involving ionic and covalent bonds.
Step 4: Analyze compound (c) SO3. Sulfur trioxide (SO3) is a molecular compound, consisting of discrete SO3 molecules held together by covalent bonds.
Step 5: Analyze compound (d) GeCl4. Germanium tetrachloride (GeCl4) is a molecular compound, consisting of discrete GeCl4 molecules held together by covalent bonds.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more nonmetals bond together through covalent bonds, sharing electrons. These compounds typically exist as discrete molecules and have relatively low melting and boiling points. Examples include water (H2O) and sulfur trioxide (SO3), which are characterized by their molecular structure and distinct molecular properties.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Naming Molecular Compounds
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds consist of positively and negatively charged ions held together by strong electrostatic forces known as ionic bonds. These compounds usually form a crystalline lattice structure, resulting in high melting and boiling points. An example is potassium aluminum silicate (KAlSi3O8), which has a three-dimensional extended structure due to the arrangement of its ions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionic Compounds Naming
Covalent Network Solids
Covalent network solids are materials where atoms are bonded by a continuous network of covalent bonds, resulting in a rigid structure. These solids exhibit high melting points and are typically hard and insoluble. An example is germanium tetrachloride (GeCl4), which can form a network structure under certain conditions, contrasting with molecular compounds that consist of individual molecules.
Recommended video:
Guided course
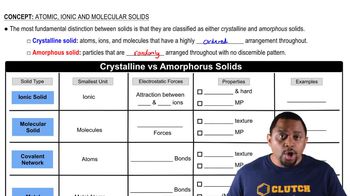
Crystalline vs Amorphous Solids
Related Practice
