Textbook Question
Write balanced equations for the formation of the following compounds from their elements.(c) Uranium hexafluoride (a solid at 25 °C)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance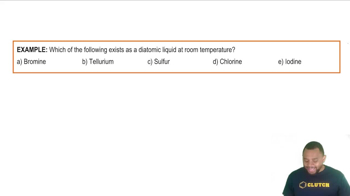
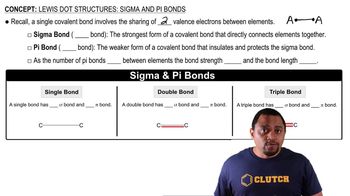
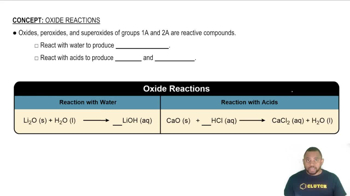
Select the group 4A element that best fits each of the following descriptions.
(c) Is the second most abundant element in the human body