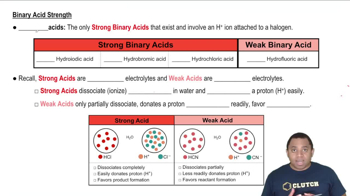
Electronegativity and Bond Strength
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. In oxyacids like HIO, HBrO, and HClO, the electronegativity of the central atom (I, Br, Cl) affects the bond strength between the hydrogen and the central atom. As electronegativity increases, the bond becomes weaker, making it easier for the acid to release H+, thus increasing acid strength.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance