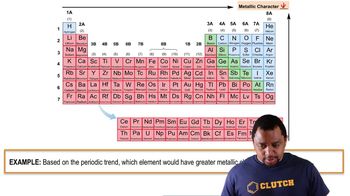
Oxide Classification
Oxides can be classified based on their properties and the elements involved. Metal oxides, such as K2O, typically exhibit higher ionic character due to the presence of metals with low electronegativity, while non-metal oxides, like SiO2 and P4O10, often have more covalent character. Recognizing these classifications aids in arranging oxides by their ionic character.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance