Textbook Question
The atomic radii of zirconium (160 pm) and hafnium (159 pm) are nearly identical. Explain.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
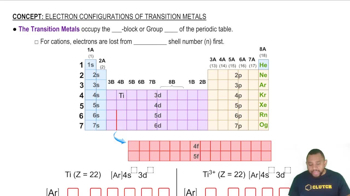

The atomic radii of zirconium (160 pm) and hafnium (159 pm) are nearly identical. Explain.
Which of the following transition metals have more than one oxidation state?
(a) Ti
(b) V
(c) Cr
(d) Zn
The highest oxidation state for the early transition metals Sc, Ti, V, Cr, and Mn is the periodic group number. The highest oxidation state for the later transition elements Fe, Co, and Ni is less than the periodic group number. Explain.