Textbook Question
Briefly account for each of the following observations:
(a) Atomic radii decrease in the order Sc > Ti > V.
(b) Densities increase in the order Ti > V > Cr.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

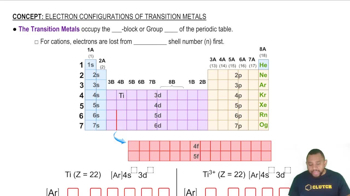
Briefly account for each of the following observations:
(a) Atomic radii decrease in the order Sc > Ti > V.
(b) Densities increase in the order Ti > V > Cr.
Arrange the following atoms in order of decreasing atomic radius, and account for the trend.
(a) Cr
(b) Ti
(c) Mn
(d) V
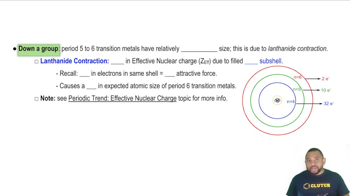
What is the lanthanide contraction, and why does it occur?