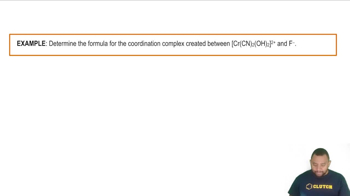
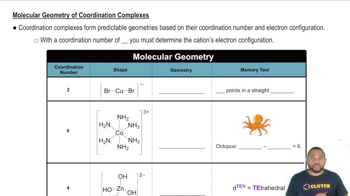
What is the formula, including the charge, for each of the following complexes?
(a) An iridium(III) complex with three ammonia and three chloride ligands
(b) A chromium(III) complex with two water and two oxalate ligands
(c) A platinum(IV) complex with two ethylenediamine and two thiocyanate ligands