Textbook Question
Draw the structure of the following complexes. What are the oxidation state, coordination number, and coordination geometry of the metal in each?
(a) Na[Au(CN)2]

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


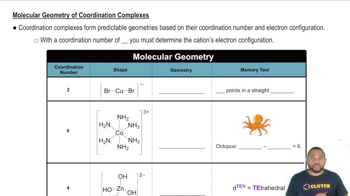
Draw the structure of the following complexes. What are the oxidation state, coordination number, and coordination geometry of the metal in each?
(a) Na[Au(CN)2]
Draw the structure of the following complexes. What are the oxidation state, coordination number, and coordination geometry of the metal in each?
(b) [Cr(NH3)2(C2O4)2]NO2
Draw the structure of the following complexes. What are the oxidation state, coordination number, and coordination geometry of the metal in each?
(a) Pt(en)2
(a) Identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base in the reaction of ethylenediamine (H2NCH2CH2NH2) with Ni2+ to form [Ni(en)3]2+.
(b) Identify the ligands and donor atoms.
(c) Give the coordination number and geometry of the metal in the complex.