Look at the colors of the isomeric complexes in Figure 21.12, and predict which is the stronger field ligand, nitro (-NO2) of nitrito (-ONO). Explain.

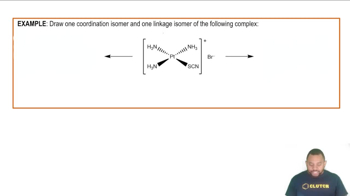
Draw the structure of all isomers of the octahedral complex [NbX2Cl4]- (X- = NCS-), and identify those that are linkage isomers.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Octahedral Complexes

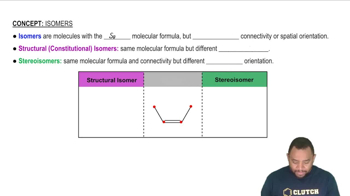
Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
Linkage Isomers
The amount of paramagnetism for a first-series transition metal complex is related approximately to its spin-only magnetic moment. The spin-only value of the magnetic moment in units of Bohr magnetons (BM) is given by sqrt(n(n + 2)), where n is the number of unpaired electrons. Calculate the spin-only value of the magnetic moment for the 2+ ions of the first-series transition metals (except Sc) in octahedral complexes with (a) weak-field ligands and (b) strong-field ligands. For which electron configurations can the magnetic moment distinguish between high-spin and low-spin electron configurations?
What hybrid orbitals are used by the metal ion and how many unpaired electrons are present the complex ion [VCl4]- with tetrahedral geometry?
(a) sp3; 2 unpaired electrons
(b) sp3; 3 unpaired electrons
(c) sp3d2; 3 unpaired electrons
(d) sp3d2; 4 unpaired electrons
Classify the following ligands as monodentate, bidentate, tri-dentate, or tetradentate. Which can form chelate rings?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
What is a racemic mixture? Does it affect plane-polarized light? Explain.
What is the name of the compound [Fe(H2O)5(SCN)]Cl2?
(a) pentaaquathiocyanatoiron(III) chloride
(b) pentaaquachlorothiocyanato iron(III)
(c) pentaaquathiocyanatoiron(III) dichloride
(d) pentaaquathiocyanatoiron(II) chloride
