Textbook Question
An H2/H+ half-cell (anode) and an Ag+/Ag half cell (cathode) are connected by a wire and a salt bridge. (c) Give the shorthand notation for the cell.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


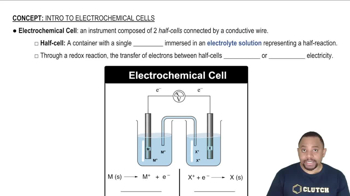
An H2/H+ half-cell (anode) and an Ag+/Ag half cell (cathode) are connected by a wire and a salt bridge. (c) Give the shorthand notation for the cell.